User guide
Administration
Manage analyzer template
Energy SOAR will display the analysis summary the same way for all analyzers: display a tag using taxonomies and level color.
List analyzer templates
The management page is accessible from the header menu through the Admin > Analyzer templates menu and required a use with the manageAnalyzerTemplate permission (refer to Profiles and permissions).
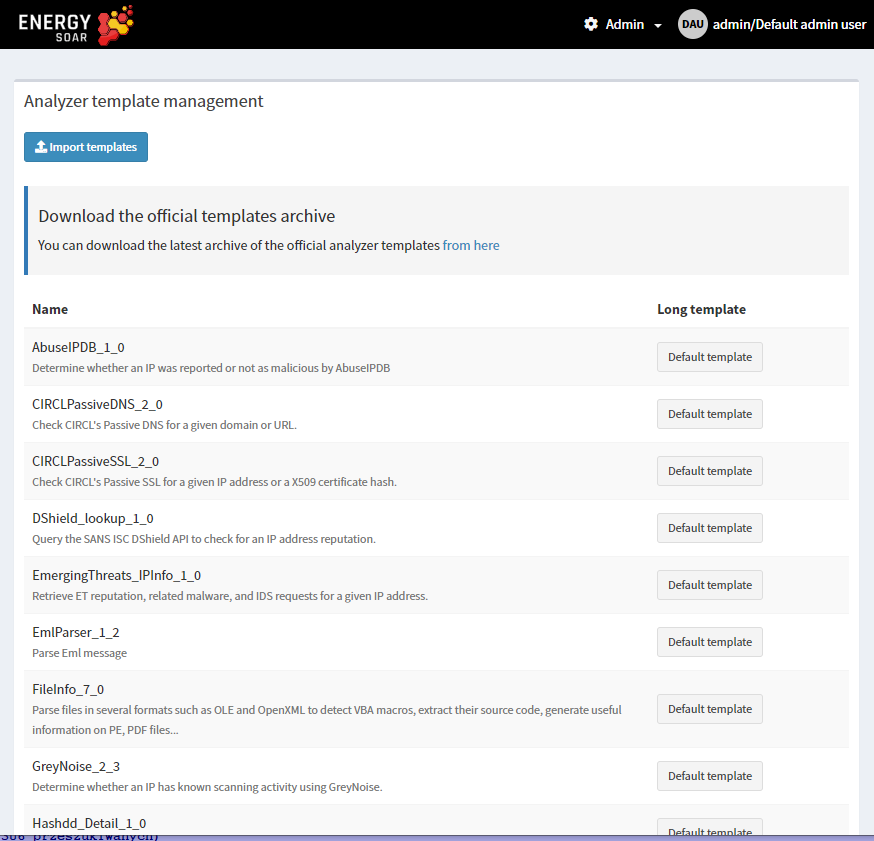
Analyzer templates are still customisable via the UI and can also be imported.
User Profiles management
Permissions
A Profile is a set of permissions attached to a User and an Organisation. It defines what the user can do on an object hold by the organisation. Energy SOAR has a finite list of permissions:
manageOrganisation (1) : the user can create, update an organisation
manageConfig (1): the user can update configuration
manageProfile (1): the user can create, update and delete profiles
manageTag (1): the user can create, update and delete tags
manageCustomField (1): the user can create, update and delete custom fields
manageCase: the user can create, update and delete cases
manageObservable: the user can create, update and delete observables
manageAlert: the user can create, update and import alerts
manageUser: the user can create, update and delete users
manageCaseTemplate: the user can create, update and delete case template
manageTask: the user can create, update and delete tasks
manageShare: the user can share case, task and observable with other organisation
manageAnalyse (2): the user can execute analyse
manageAction (2): the user can execute actions
manageAnalyzerTemplate (2): the user can create, update and delete analyzer template (previously named report template)
manageWorkflows: the user can create, update and delete workflows
listWorkflows: the user can see a list of workflows
viewWorkflows: the user can see workflow details
manageReports: the user can create, update and delete reports
listReports: the user can see a list of reports
(1) Organisations, configuration, profiles and tags are global objects. The related permissions are effective only on “admin” organisation. (2) Actions, analysis and template is available only if Energy SOAR Automation connector is enabled
NOTE
Read information doesn’t require specific permission. By default, users in an organisation can see all data shared with that organisation (cf. shares, discussed in Organisations,Users and sharing).
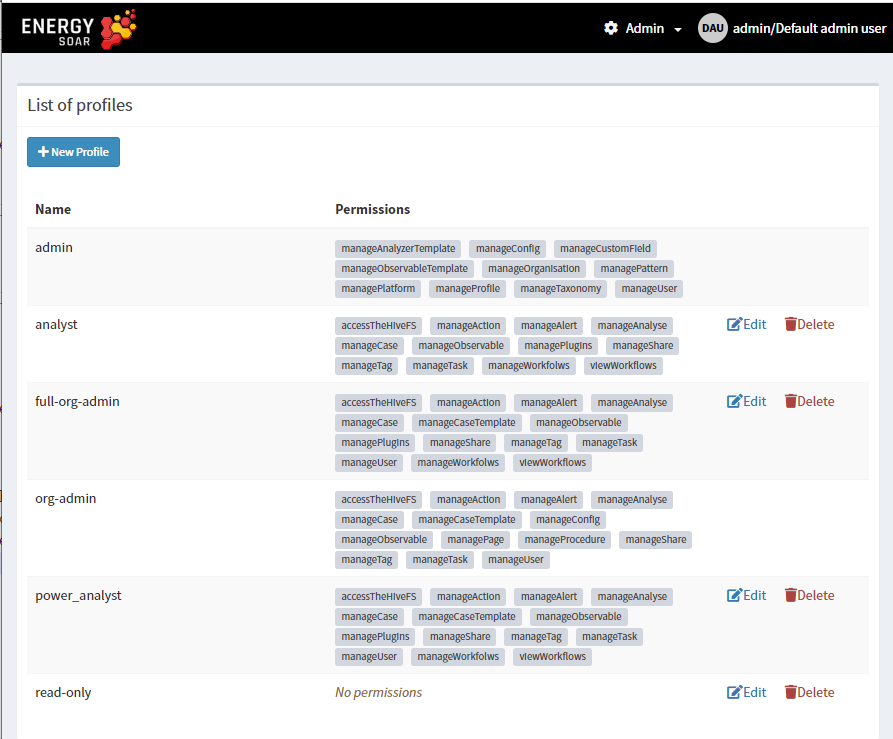
Profiles
We distinguish two types of profiles:
Administration Profiles
Organisation Profiles
The management page is accessible from the header menu through the Admin > Profiles menu and required a use with the manageProfile permission (refer to the section above).
Energy SOAR comes with default profiles but they can be updated and removed (if not used). New profiles can be created.
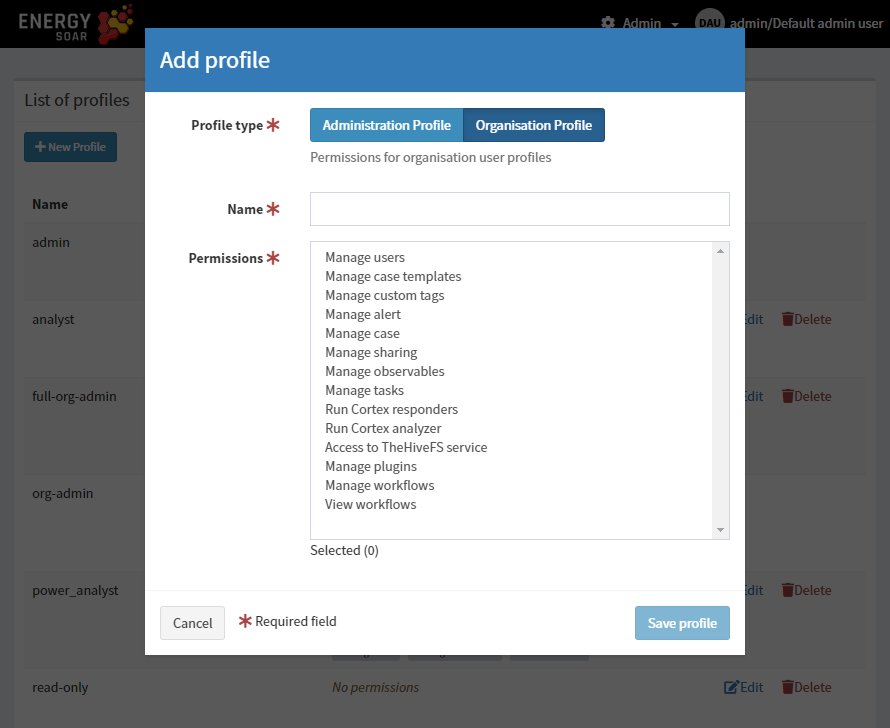
Once the New Profile button is clicked, a dialog is opened asking for the profile type, a name for the profile and a selection of permissions. Multiple selection can be made using CTRL+click.
If it is used, a profile can’t be remove but can be updated.
Default profiles are:
admin: can manage all global objects and users. Can’t create case.
analyst: can manage cases and other related objects (observables, tasks, …), including shring them
org-admin: all permissions except those related to global objects
read-only: no permission
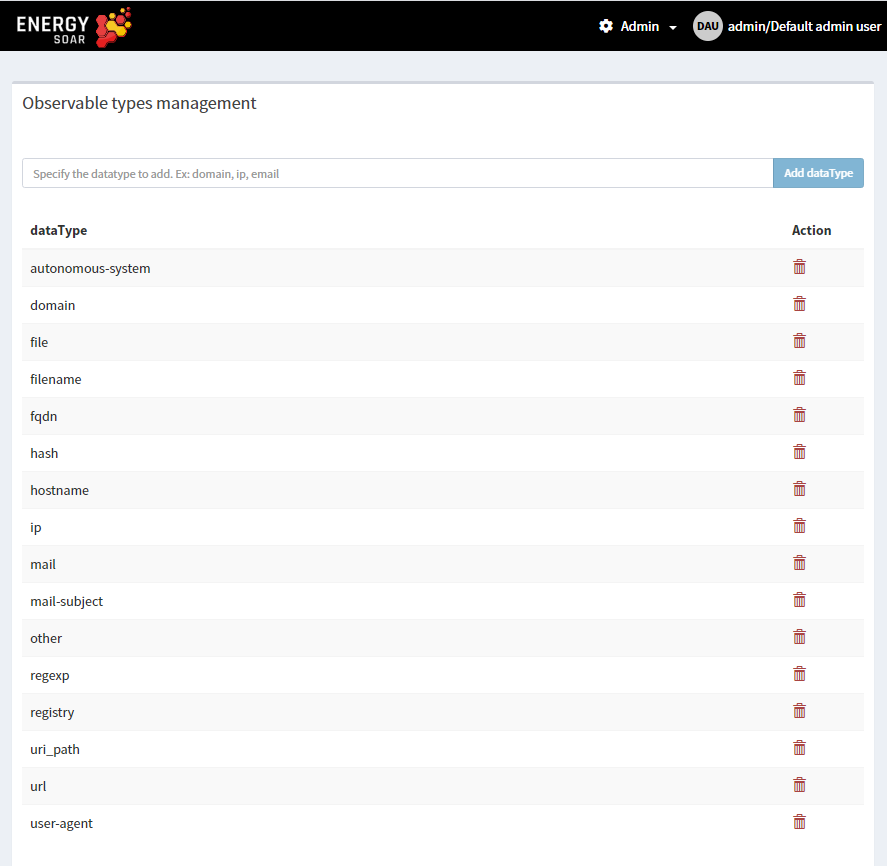
Observable types
You can edit observable types in the administrator panel.
Admin > Observable
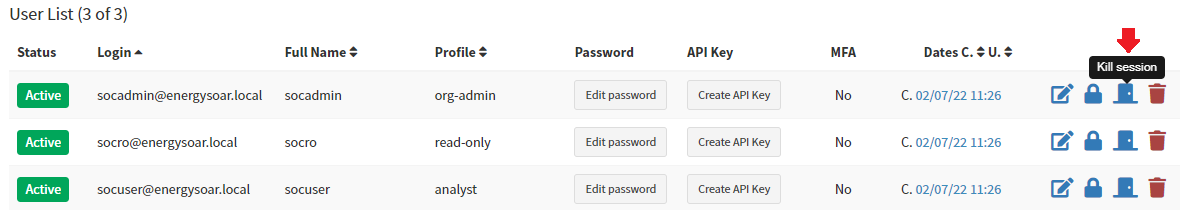
Kill user session
Everytime you can manage logged user sessions as admin user. In organizations administration page you can kill user session. This user will be immediatelly logout.
Select user organization
And click “Kill session” button.
Reports
Create and edit
Go to Reports on top menu
Click Create new report on the left
Now you can see New Report view.
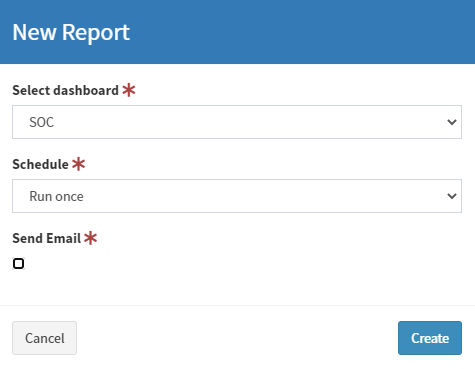
Select dashboard: there you should select exising dashboard.
Schedule types:
Run once
Daily
Weekly
Montly
Cron format (UNIX cron format)
Send Email: select if you would like to recive report on e-mail.
List
On reports list you see all created reports.
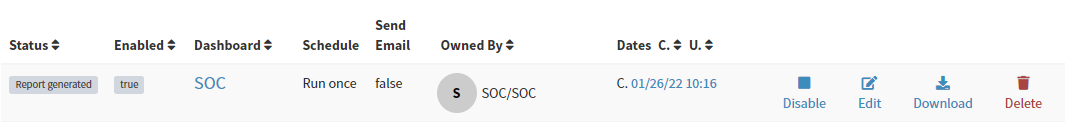
Reports statuses:
Created: Going to create the report
Generated: Report was generated and you can download or it was sent
Error: An error occurs. Please check logs
Actions:
Enable/Disable
Edit
Download
Delete
Cases
Observables
Observables are pieces of information added to a case.
| autonomous-system | fqdn | registry | |
| domain | hash | mail-subject | uri_path |
| file | hostname | other | url |
| filename | ip | regexp | user-agent |
How to add observables into Case
Perform the following steps to add an observable:
Click Add observable(s) button:

Create new observable(s) window appears:
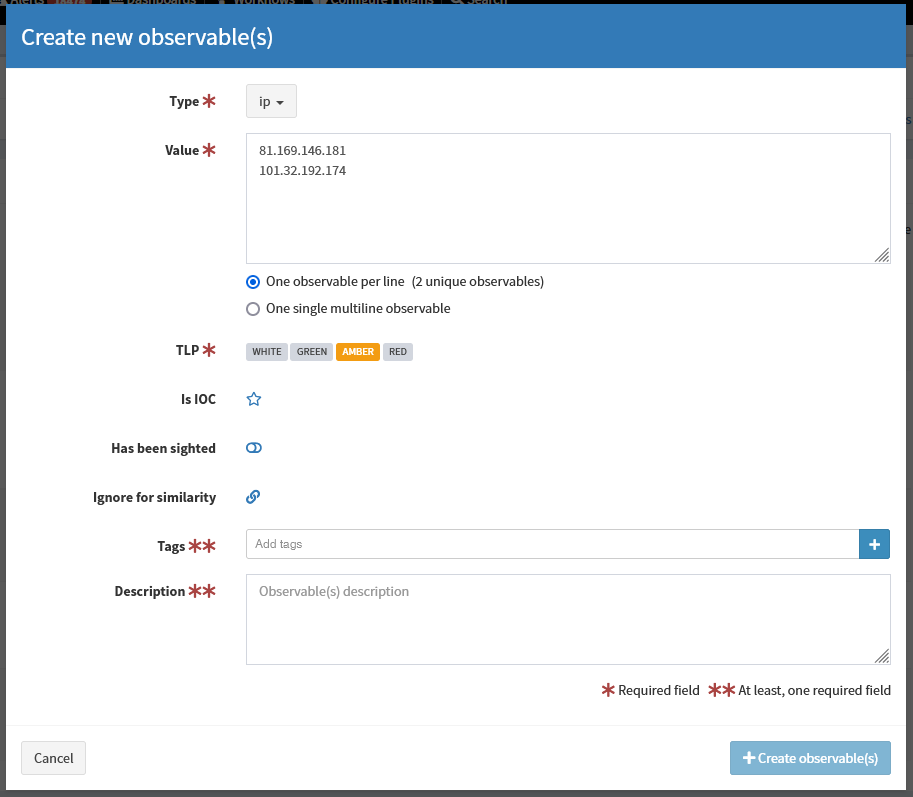
Select type e.g. ip, domain, url, mail. If you choose file type, you can upload a file. Zipped archives are supported.

You can add one single observables or many observables at once - one observable per line.
Select appropriate TLP flag.
(Optional) IOC flag indicates observables classified as True Positive. Only IOC-flagged observables are exported to MISP instances.
(Optional) You can also set “Has been sighted” toggle to mark observables which have been seen.
(Optional) If you click “Ignore for similarity”, you will disable “Observable seen in other cases” list.
Add tags and/or description.
Click Create observable(s). On Observable List you can check if observables have been seen in other cases:
Black eye: Observable seen in other cases,
Red eye: Observable seen in other cases and flagged as IOC there.
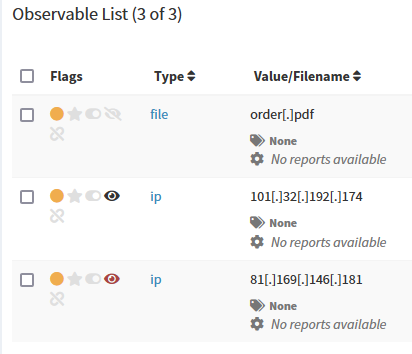
You can display details and check cases where the observable has been seen:
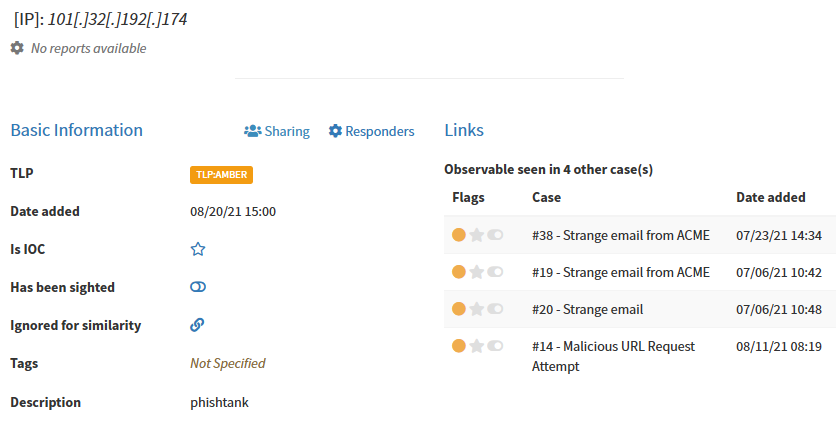
After uploading file-type observables hashes are automatically calculated:
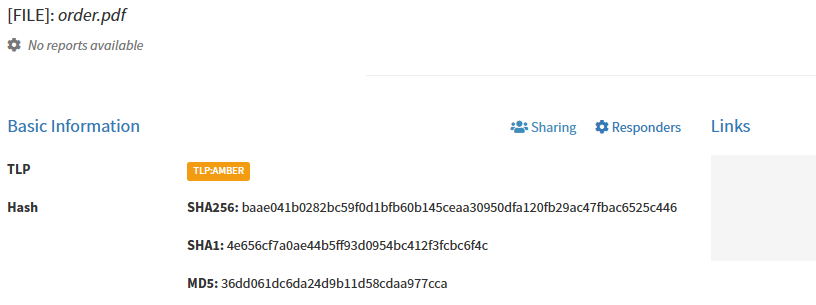
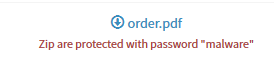
If you want to download file observable, it will be zipped and password protected:
You can run various analyzers (e.g. VirusTotal, MaxMind_GeoIP) and responders (e.g. block IP, domain, e-mail) against observables.
Organisation
Reports
Workflows
SOC analysts have to handle many repetitive tasks. With Energy SOAR you can build workflows to automatically execute all relevant actions.
Workflows helps you to interconnect different apps with an API with each other to share and manipulate its data without a single line of code. It is an easy to use, user-friendly and highly customizable module, which uses an intuitive user interface for you to design your unique scenarios very fast. A workflow is a collection of nodes connected together to automate a process. A workflow can be started manually (with the Start node) or by Trigger nodes. When a workflow is started, it executes all the active and connected nodes. The workflow execution ends when all the nodes have processed their data. You can view your workflow executions in the Execution log, which can be helpful for debugging.
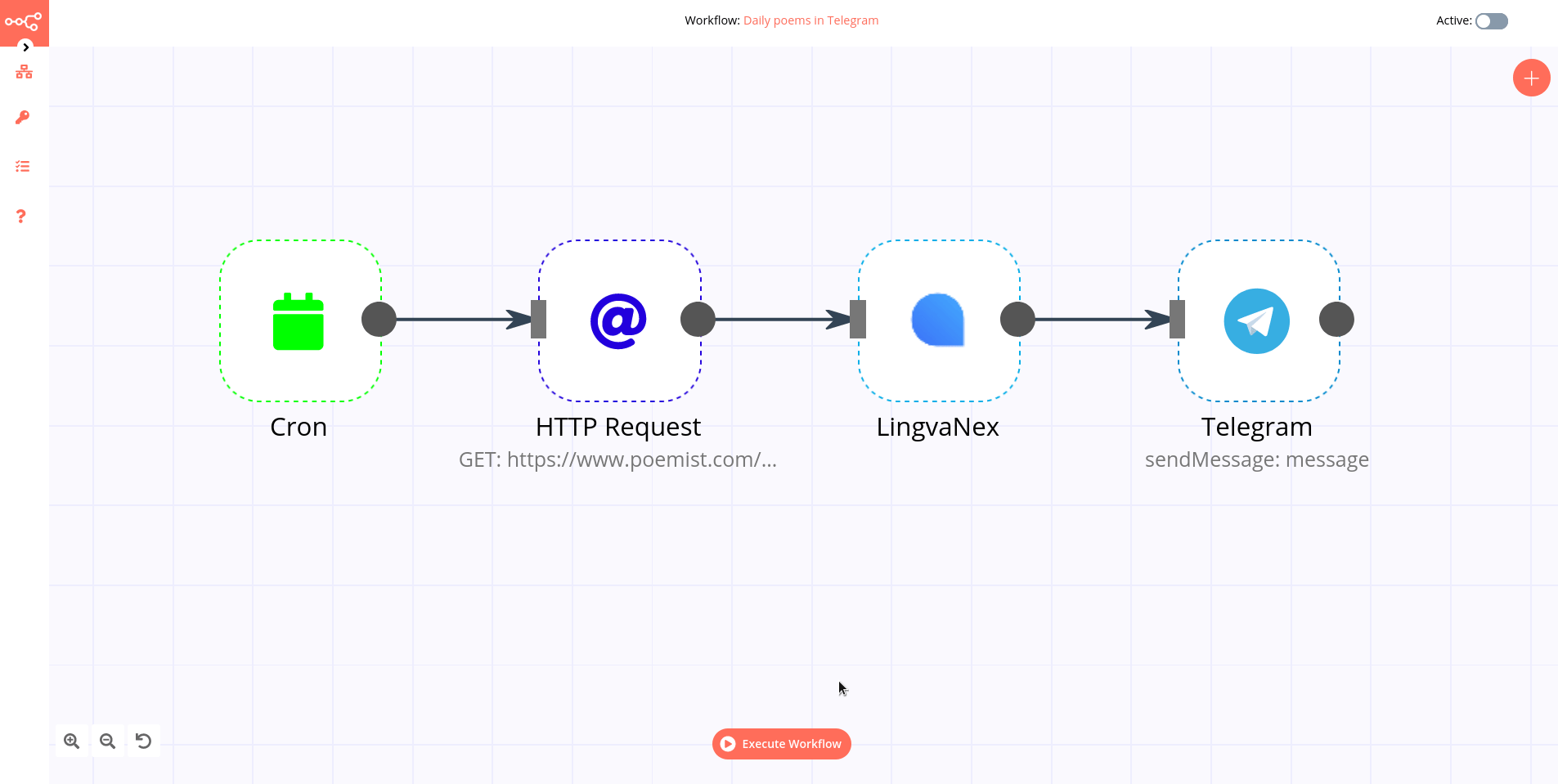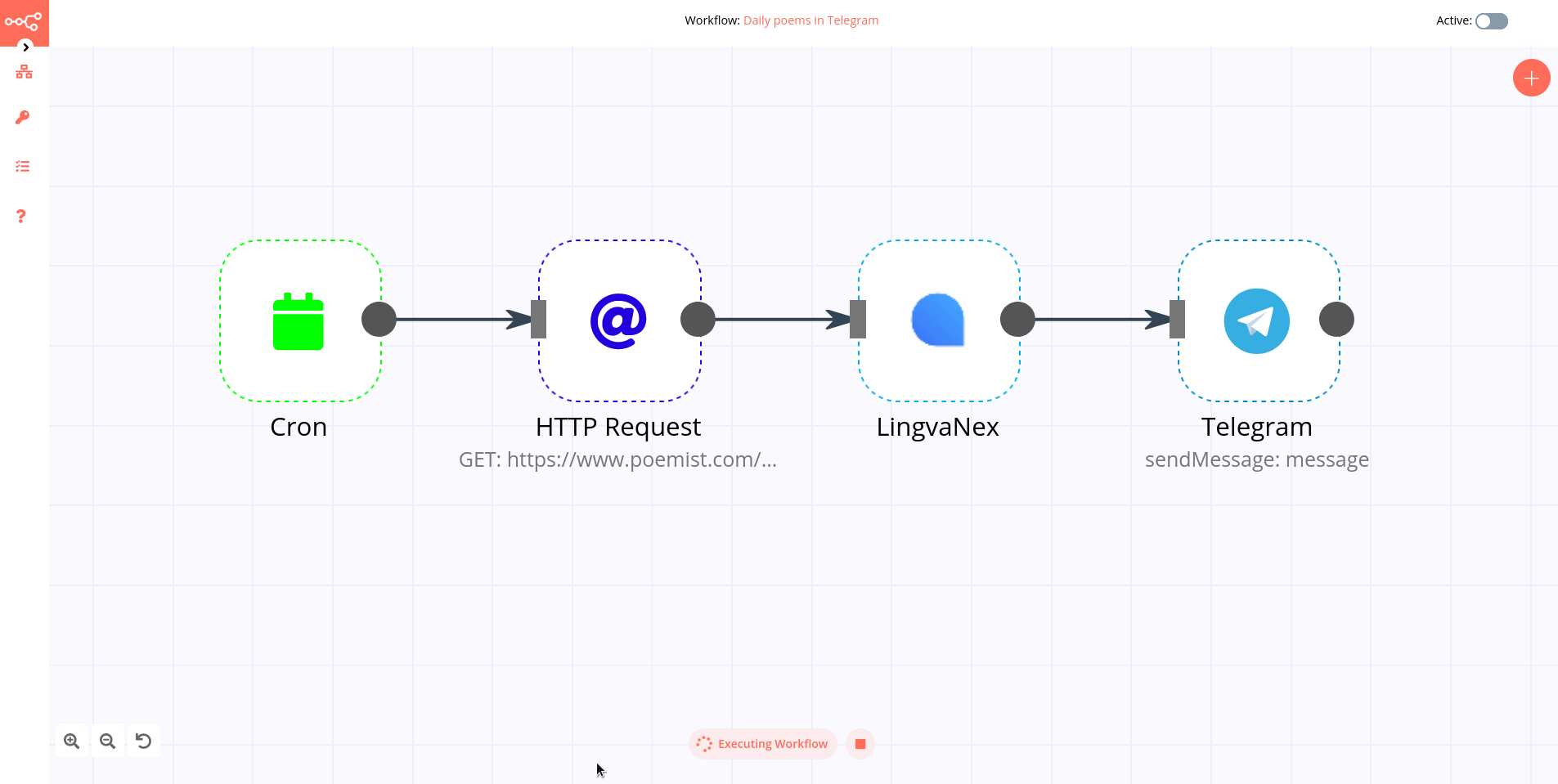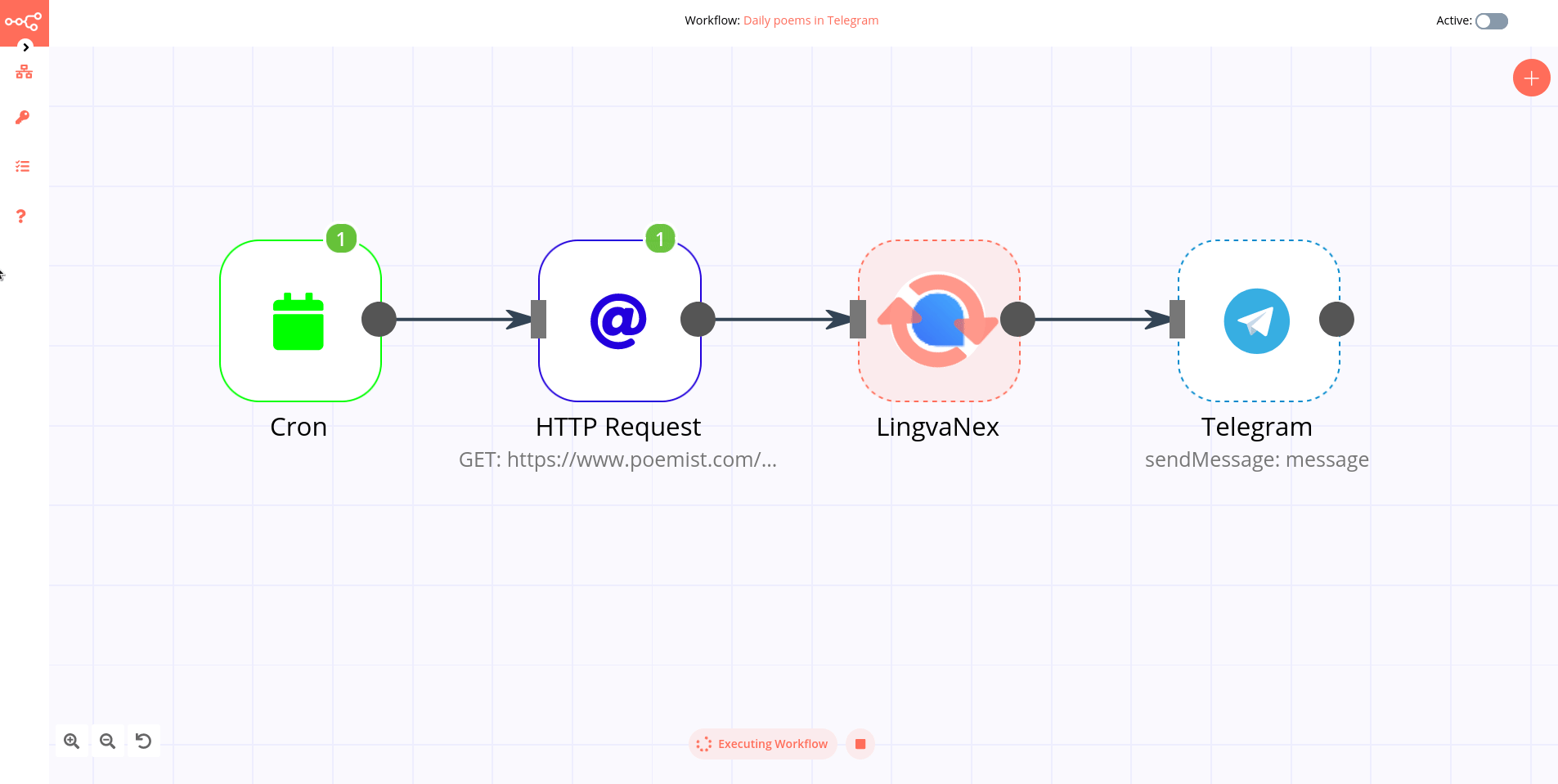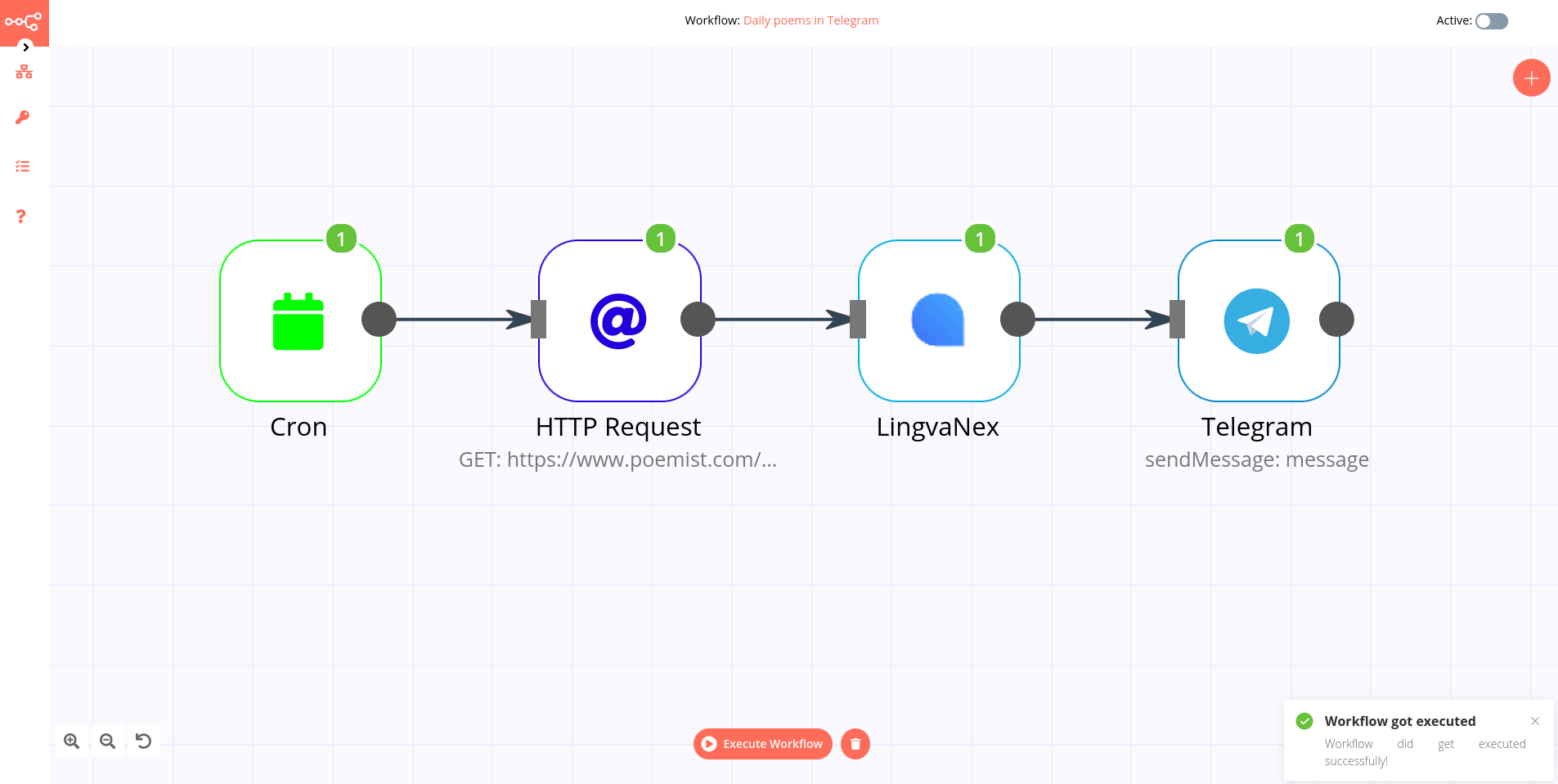
Activating a workflow Workflows that start with a Trigger node or a Webhook node need to be activated in order to be executed. This is done via the Active toggle in the Workflow UI. Active workflows enable the Trigger and Webhook nodes to receive data whenever a condition is met (e.g., Monday at 10:00, an update in a Trello board) and in turn trigger the workflow execution. All the newly created workflows are deactivated by default.
Sharing a workflow
Workflows are saved in JSON format. You can export your workflows as JSON files or import JSON files into your system. You can export a workflow as a JSON file in two ways:
Download: Click the Download button under the Workflow menu in the sidebar. This will download the workflow as a JSON file.
Copy-Paste: Select all the workflow nodes in the Workflow UI, copy them (Ctrl + c), then paste them (Ctrl + v) in your desired file. You can import JSON files as workflows in two ways:
Import: Click Import from File or Import from URL under the Workflow menu in the sidebar and select the JSON file or paste the link to a workflow.
Copy-Paste: Copy the JSON workflow to the clipboard (Ctrl + c) and paste it (Ctrl + v) into the Workflow UI.
Workflow settings
On each workflow, it is possible to set some custom settings and overwrite some of the global default settings from the Workflow > Settings menu.
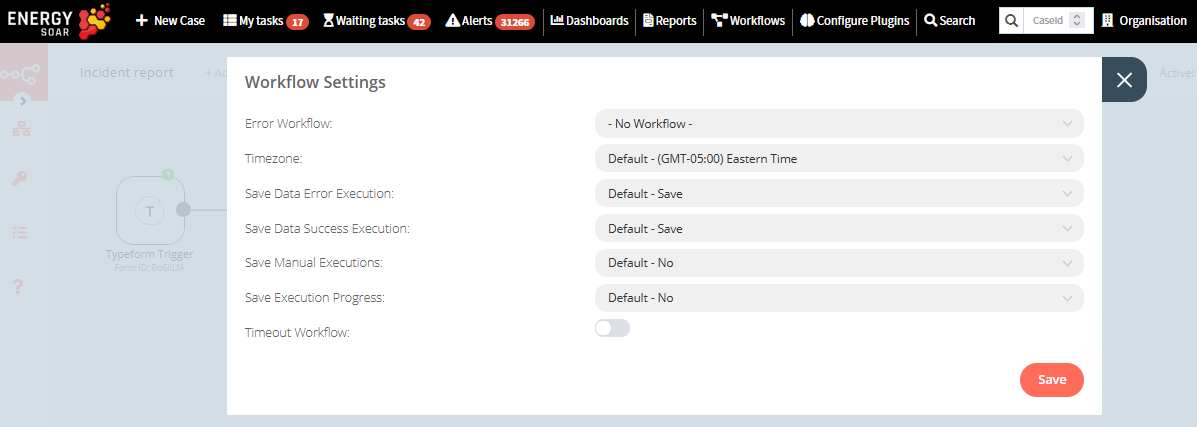
The following settings are available:
Error Workflow: Select a workflow to trigger if the current workflow fails.
Timezone: Sets the timezone to be used in the workflow. The Timezone setting is particularly important for the Cron Trigger node.
Save Data Error Execution: If the execution data of the workflow should be saved when the workflow fails.
Save Data Success Execution: If the execution data of the workflow should be saved when the workflow succeeds.
Save Manual Executions: If executions started from the Workflow UI should be saved.
Save Execution Progress: If the execution data of each node should be saved. If set to “Yes”, the workflow resumes from where it stopped in case of an error. However, this might increase latency.
Timeout Workflow: Toggle to enable setting a duration after which the current workflow execution should be cancelled.
Timeout After: Only available when Timeout Workflow is enabled. Set the time in hours, minutes, and seconds after which the workflow should timeout.
Failed workflows
If your workflow execution fails, you can retry the execution. To retry a failed workflow:
Open the Executions list from the sidebar.
For the workflow execution you want to retry, click on the refresh icon under the Status column.
Select either of the following options to retry the execution:
Retry with currently saved workflow: Once you make changes to your workflow, you can select this option to execute the workflow with the previous execution data.
Retry with original workflow: If you want to retry the execution without making changes to your workflow, you can select this option to retry the execution with the previous execution data.
You can also use the Error Trigger node, which triggers a workflow when another workflow has an error. Once a workflow fails, this node gets details about the failed workflow and the errors.
Crate your first workflow
Automate Incident Reporting with Typeform
Let’s create your first workflow in Energy SOAR. The workflow will create a new alert and promote it to a case whenever a user submits a high severity incident.
Prerequisites
You’ll need to obtain the credentials for the Typeform Trigger node.
Create a Typeform account: https://www.typeform.com/
Open the Typeform dashboard: https://admin.typeform.com/
Click on your avatar on the top right and select ‘Settings’.
Click on Personal tokens under the Profile section in the sidebar.
Click on the Generate a new token button.
Enter a name in the Token name field.
Click on the Generate token button.
Click on the Copy button to copy the access token.
In Energy SOAR choose Workflows > Credentials > New > Typeform API.
Enter a name for your credentials in the Credentials Name field.
Paste the access token in the Access Token field.
Click the Create button to save your credentials in Energy SOAR.
You will also need to create a form in Typeform to collect incident reports with the following questions:
What is your name? (optional) (Short Text)
What is your email address? (optional) (Email)
What is incident’s category? (Multiple Choice)

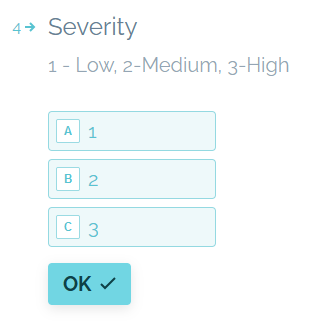
Severity (Multiple Choice)
Description (Long Text)
Building the Workflow
This workflow would use the following nodes:
Typeform Trigger - Start the workflow when a form receives a report
Set - Set the workflow data
FunctionItem - Calculate severity and alert reference
Energy SOAR Base - Create alert and case
IF - Conditional logic to decide the flow of the workflow
NoOp - Do nothing (optional)
The final workflow should look like the following image:
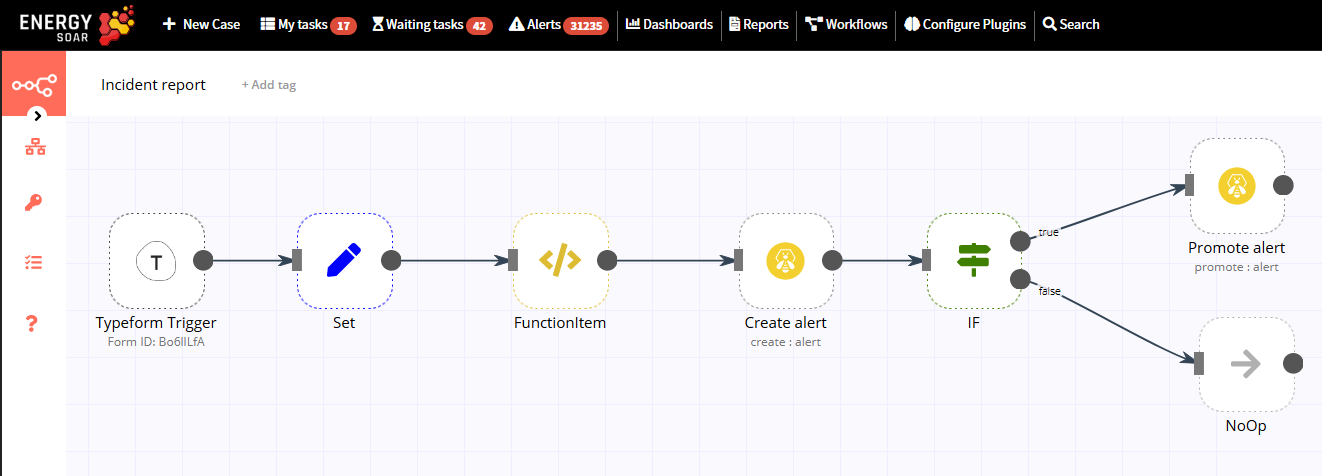
Typeform Trigger node
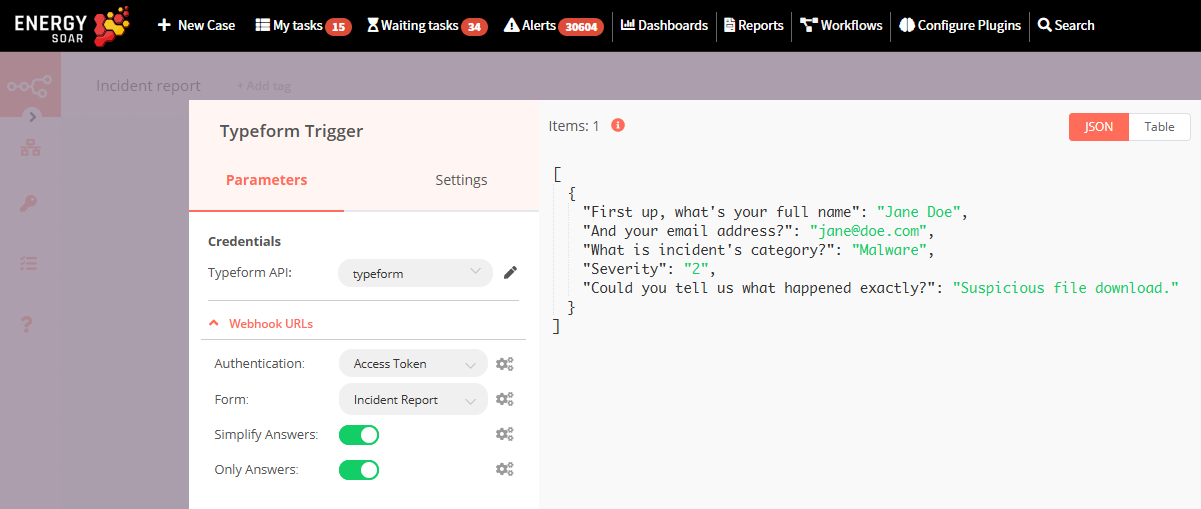
We’ll use the Typeform Trigger node for starting the workflow. Add a Typeform Trigger node by clicking on the + button on the top right of the Workflow UI. Click on the Typeform Trigger node under the section marked Trigger.
Double click on the node to enter the Node Editor. Select Credentials from the Typeform API dropdown list.
Select the form that you created from the Form dropdown list. We’ll let the other fields stay as they are.
Now save your workflow so that the webhook in the Typeform Trigger node can be activated. Since you’ll be using the test webhooks while building the workflow, the node only stays active for 120 seconds after you click the Execute Node button.
After clicking on the Execute Node button, submit a response to your form in Typeform.
Set node
We’ll use the Set node to ensure that only the data that we set in this node gets passed on to the next nodes in the workflow.
Add the Set node by clicking on the + button and selecting the Set node. Click on Add Value and select String from the dropdown list. Enter title in the Name field. Since the Value (title) would be a dynamic piece of information, click on the gears icon next to the field, and select Add Expression.
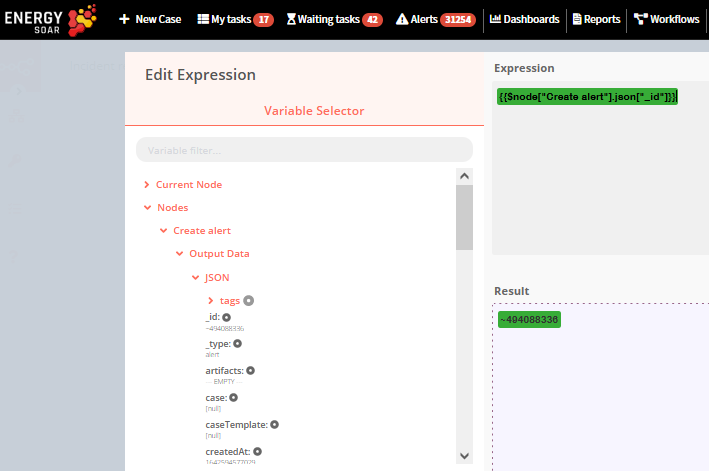
This will open up the Variable Selector. From the left panel, select the following variable: Nodes > Typeform Trigger > Output Data > JSON > What is incident’s category? Also add Incident Report prefix, so the expression would look like this: Incident Report - {{$node[“Typeform Trigger”].json[“What is incident’s category?”]}}
Close the Edit Expression window. Click on Add Value and select String from the dropdown list. Enter description in the Name field. Since the Value (description) would be a dynamic piece of information, click on the gears icon next to the field, and select Add Expression. This will open up the Variable Selector. From the left panel, select the following variables: Nodes > Typeform Trigger > Output Data > JSON > What is your name? Nodes > Typeform Trigger > Output Data > JSON > What is your email address? Nodes > Typeform Trigger > Output Data > JSON > Description?
Also add Name, E-mail, Details prefixes. Full expression:
Name: {{$node["Typeform Trigger"].json["First up, what's your full name"]}}
E-mail: {{$node["Typeform Trigger"].json["And your email address?"]}}
Details: {{$node["Typeform Trigger"].json["Could you tell us what happened exactly?"]}}
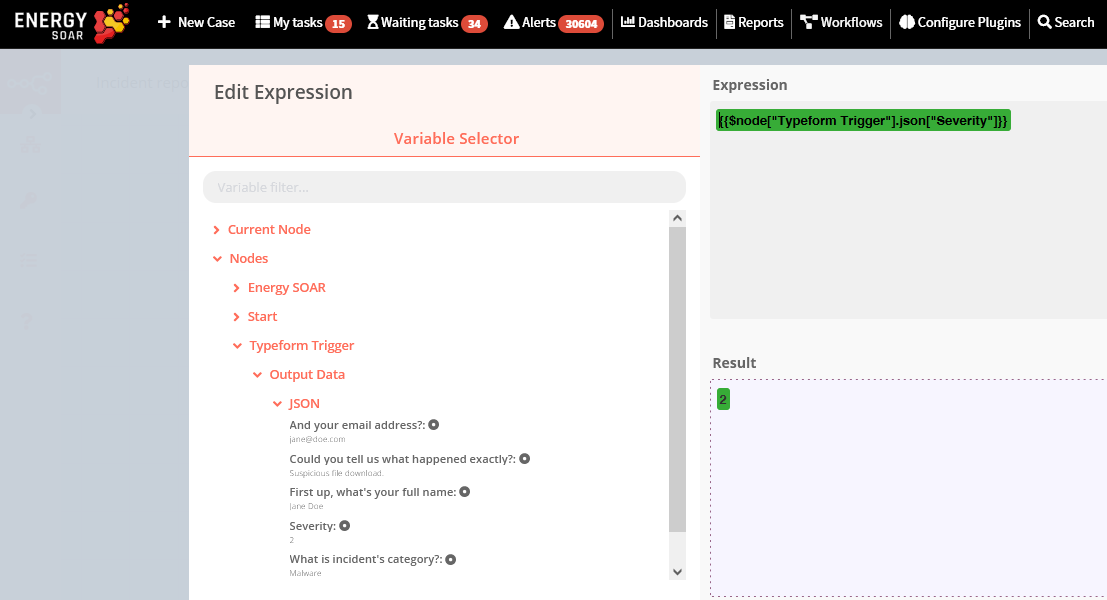
Close the Edit Expression window. Click on Add Value and select Number from the dropdown list. Enter severity in the Name field. Since the Value (severity) would be a dynamic piece of information, click on the gears icon next to the field, and select Add Expression. This will open up the Variable Selector. Delete the 0 in the Expression field on the right. From the left panel, select the following variable: Nodes > Typeform Trigger > Output Data > JSON > Severity Toggle Keep Only Set to true. We set this option to true to ensure that only the data that we have set in this node get passed on to the next nodes in the workflow. Click on the Execute Node button on the top right to set the data for the workflow.
FunctionItem node
To create Energy SOAR alert in workflow we have to provide SourceRef number. We’ll use the FunctionItem node to generate that random number. Add the FunctionItem node by clicking on the + button and selecting the FunctionItem node. Clear JavaScript Code window and insert the following code:
function getRandomInt(max) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * max);
}
item.number= getRandomInt(20000000);
item.number=item.number.toString(16);
item.severity=parseInt(item.severity);
return item;
We use parseInt function to convert string severity value into an integer.
Create alert node Add Energy SOAR Base node by clicking on the + button and selecting the Energy SOAR Base node. Double click on the node and click on Energy SOAR Base name to change it to Create alert.
Since the Title would be a dynamic piece of information, click on the gears icon next to the field, and select Add Expression.
This will open up the Variable Selector. From the left panel, select the following variable: Nodes > Set > Output Data > JSON > title
Close the Edit Expression window. In Description field add expression: Nodes > Set > Output Data > JSON > description
Close the Edit Expression window. In Severity field add expression: Nodes > FunctionItem > Output Data > JSON > severity
Close the Edit Expression window. In SourceRef field add expression: Nodes > FunctionItem > Output Data > JSON > number
Click on the Execute Node button on the top right to create alert.
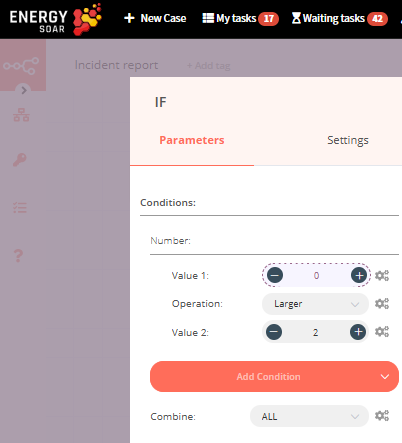
IF node Add the IF node by clicking on the + button and selecting the IF node. This is a conditional logic node that allows us to alter the flow of the workflow depending on the data that we get from the previous node(s). Double click on the node, click on the Add Condition button and select Number from the menu. Since the Value 1 (severity) would be a dynamic piece of information, click on the gears icon next to the field, and select Add Expression. This will open up the Variable Selector. Delete the 0 in the Expression field on the right. From the left panel, select the following variable: Nodes > Create alert > Output Data > JSON > severity For the Operation field, we’ll set it to ‘Larger’. For Value 2, enter 2. This will ensure that the IF node returns true only if the severity is higher than 2 (above medium level). Feel free to change this to some other value. Click on the Execute Node button on the top right to check if the severity is larger than 2 or not.
Promote alert node
Add Energy SOAR Base node by clicking on the + button and selecting the Energy SOAR node. Double click on the node and click on Energy SOAR name to change it to Promote alert.
Select ‘Promote’ from the Operation dropdown list. In Alert ID field add expression: Nodes > Create alert > Output Data > JSON > _id
NoOp node If the score is smaller than 3, we don’t want the workflow to do anything. We’ll use the NoOp node for that. Adding this node here is optional, as the absence of this node won’t make a difference to the functioning of the workflow. Add the NoOp node by clicking on the + button and selecting the NoOp node. Connect this node with the false output of the IF node. To test the workflow, click on the Execute Workflow button at the bottom of the Workflow UI. Don’t forget to save the workflow and then click on the Activate toggle on the top right of the screen to set it to true and activate the workflow. Green checkmarks indicate successful workflow execution:
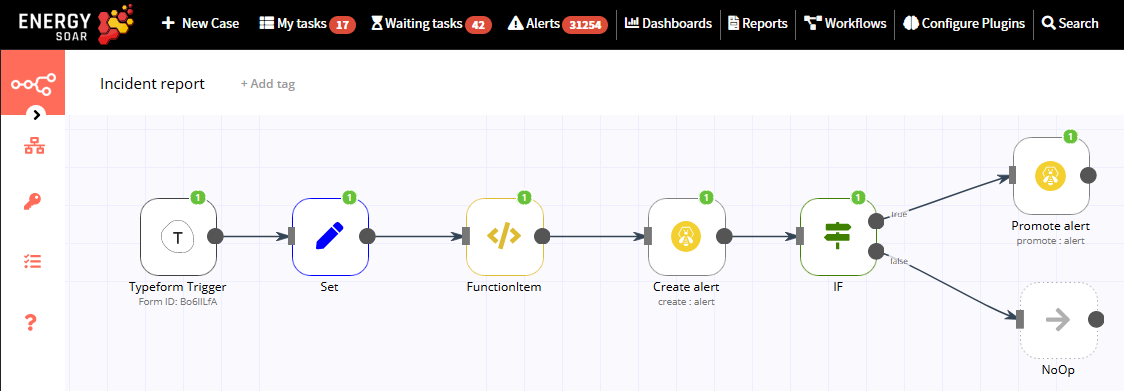
Congratulations on creating you first workflow with Energy SOAR.
Connection
A connection establishes a link between nodes to route data through the workflow. A connection between two nodes passes data from one node’s output to another node’s input. Each node can have one or multiple connections.
To create a connection between two nodes, click on the grey dot on the right side of the node and slide the arrow to the grey rectangle on the left side of the following node.
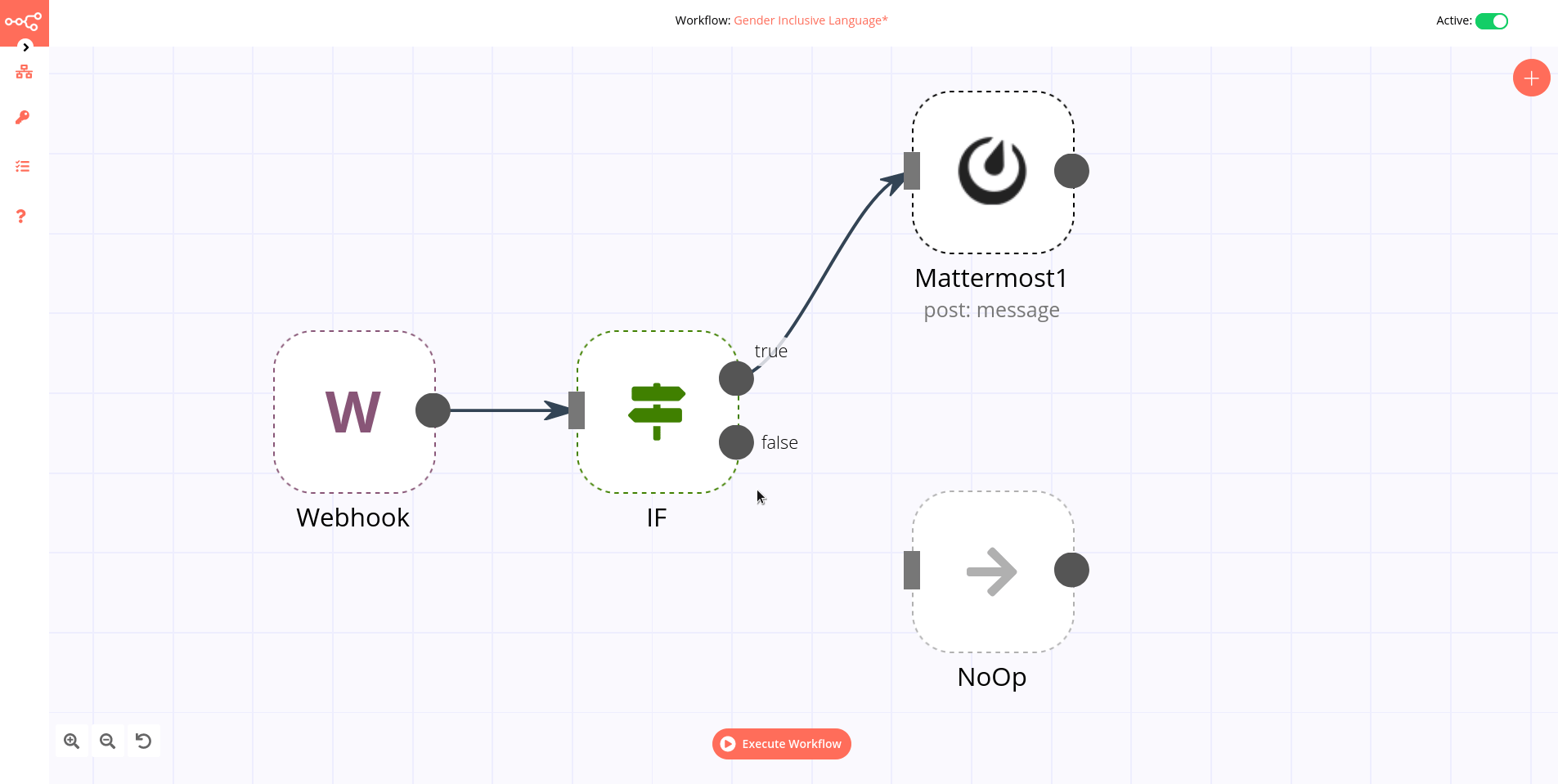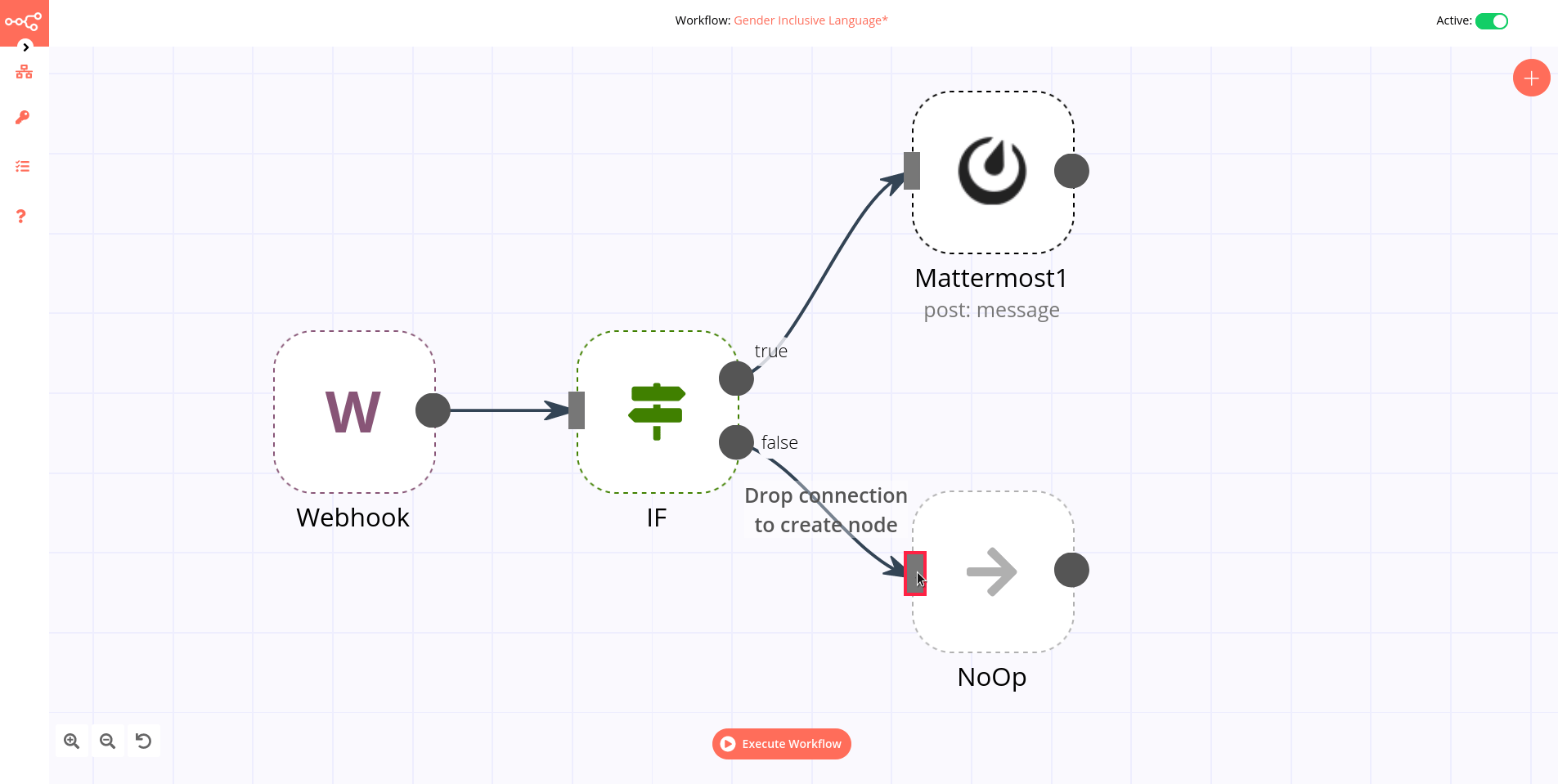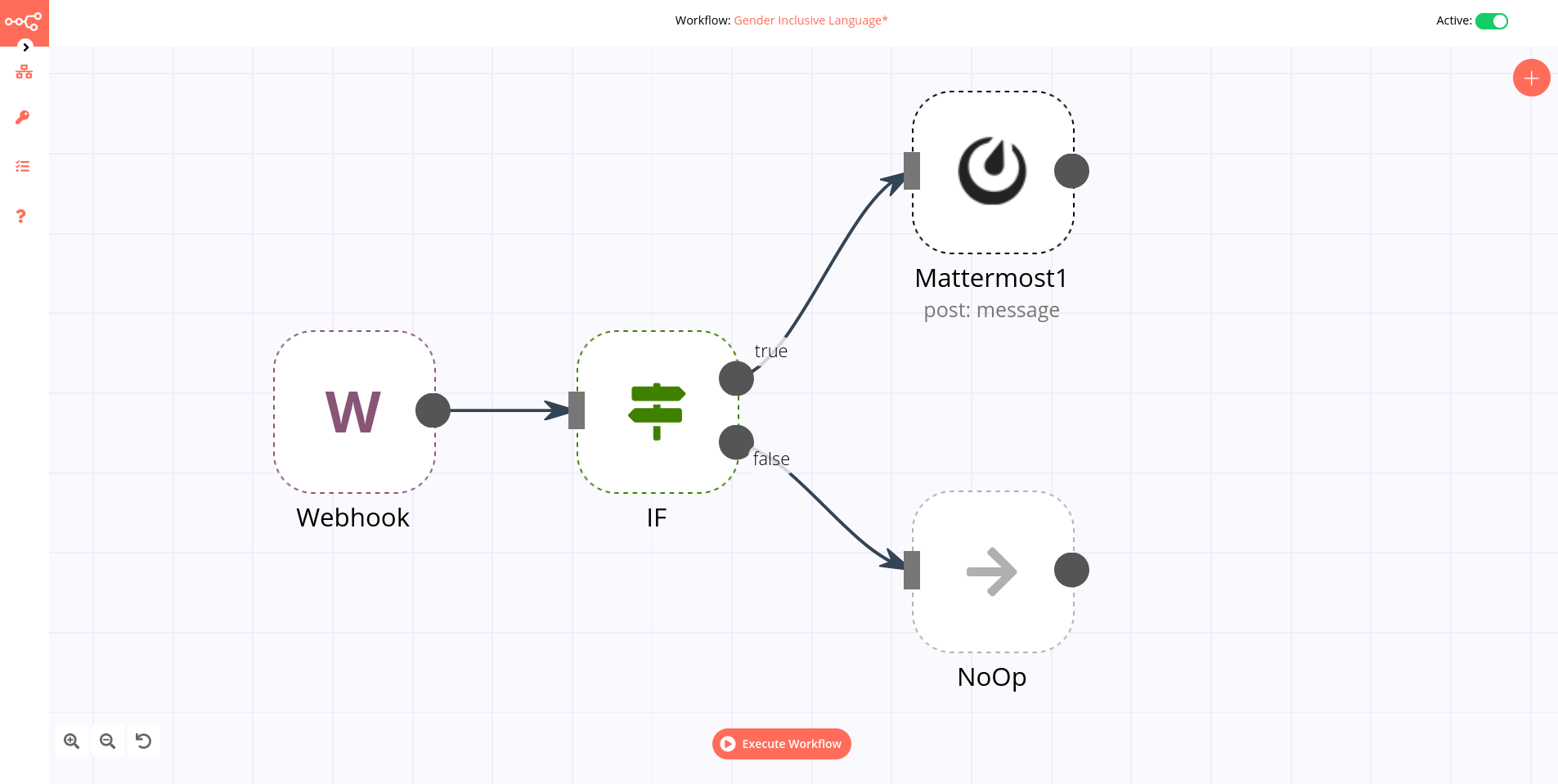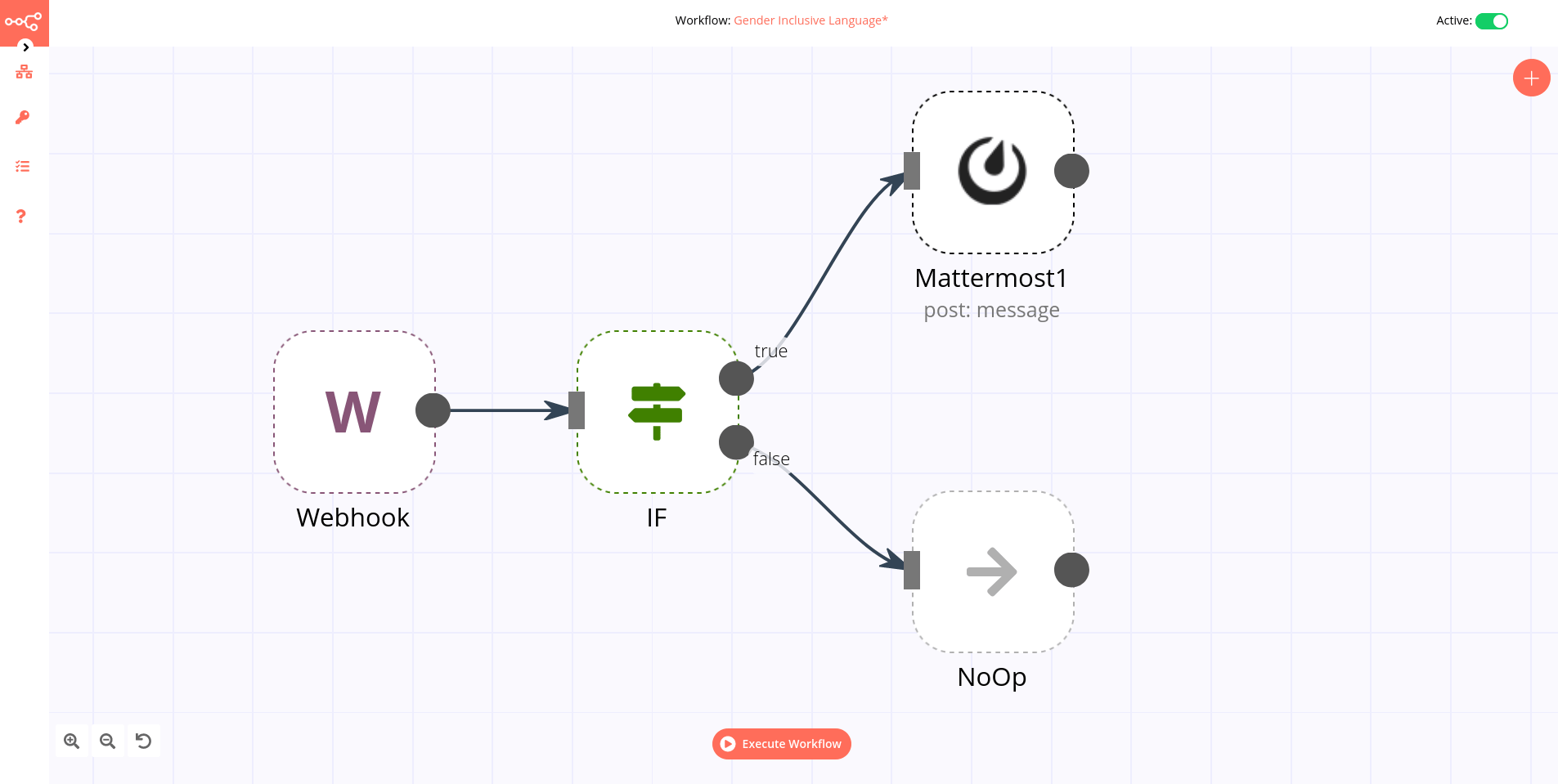
Example
An IF node has two connections to different nodes: one for when the statement is true and one for when the statement is false.
Workflows List
This section includes the operations for creating and editing workflows.
New: Create a new workflow
Open: Open the list of saved workflows
Save: Save changes to the current workflow
Save As: Save the current workflow under a new name
Rename: Rename the current workflow
Delete: Delete the current workflow
Download: Download the current workflow as a JSON file
Import from URL: Import a workflow from a URL
Import from File: Import a workflow from a local file
Settings: View and change the settings of the current workflow
Credentials
This section includes the operations for creating credentials.
Credentials are private pieces of information issued by apps/services to authenticate you as a user and allow you to connect and share information between the app/service and the n8n node.
New: Create new credentials
Open: Open the list of saved credentials
Executions
This section includes information about your workflow executions, each completed run of a workflow.
You can enabling logging of your failed, successful, and/or manually selected workflows using the Workflow > Settings page.
Node
A node is an entry point for retrieving data, a function to process data, or an exit for sending data. The data process performed by nodes can include filtering, recomposing, and changing data.
There may be one or several nodes for your API, service, or app. By connecting multiple nodes, you can create simple and complex workflows. When you add a node to the Editor UI, the node is automatically activated and requires you to configure it (by adding credentials, selecting operations, writing expressions, etc.).
There are three types of nodes:
Core Nodes
Regular Nodes
Trigger Nodes
Core nodes
Core nodes are functions or services that can be used to control how workflows are run or to provide generic API support.
Use the Start node when you want to manually trigger the workflow with the Execute Workflow button at the bottom of the Editor UI. This way of starting the workflow is useful when creating and testing new workflows.
If an application you need does not have a dedicated Node yet, you can access the data by using the HTTP Request node or the Webhook node. You can also read about creating nodes and make a node for your desired application.
Regular nodes
Regular nodes perform an action, like fetching data or creating an entry in a calendar. Regular nodes are named for the application they represent and are listed under Regular Nodes in the Editor UI.
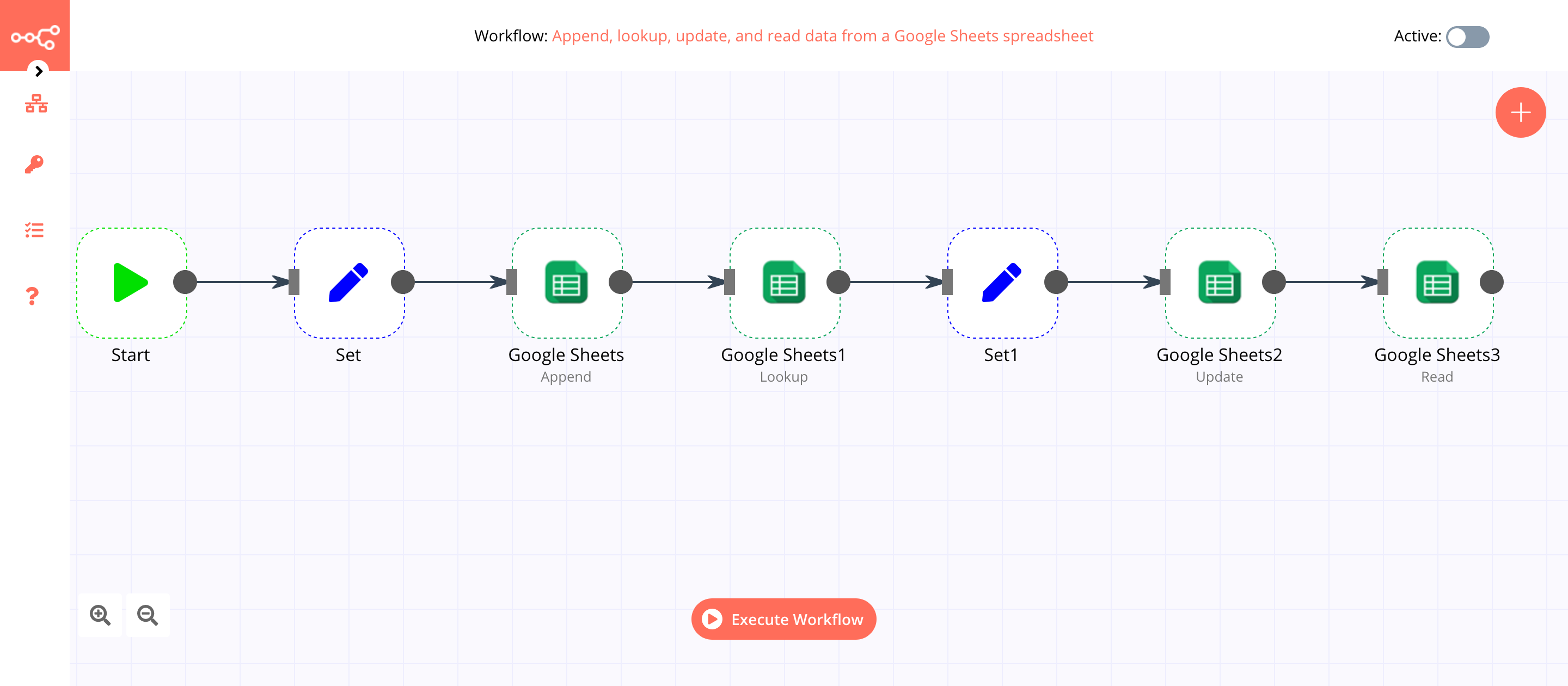
Example
A Google Sheets node can be used to retrieve or write data to a Google Sheet.
Trigger nodes
Trigger nodes start workflows and supply the initial data.
Trigger nodes can be app or core nodes.
Core Trigger nodes start the workflow at a specific time, at a time interval, or on a webhook call. For example, to get all users from a Postgres database every 10 minutes, use the Interval Trigger node with the Postgres node.
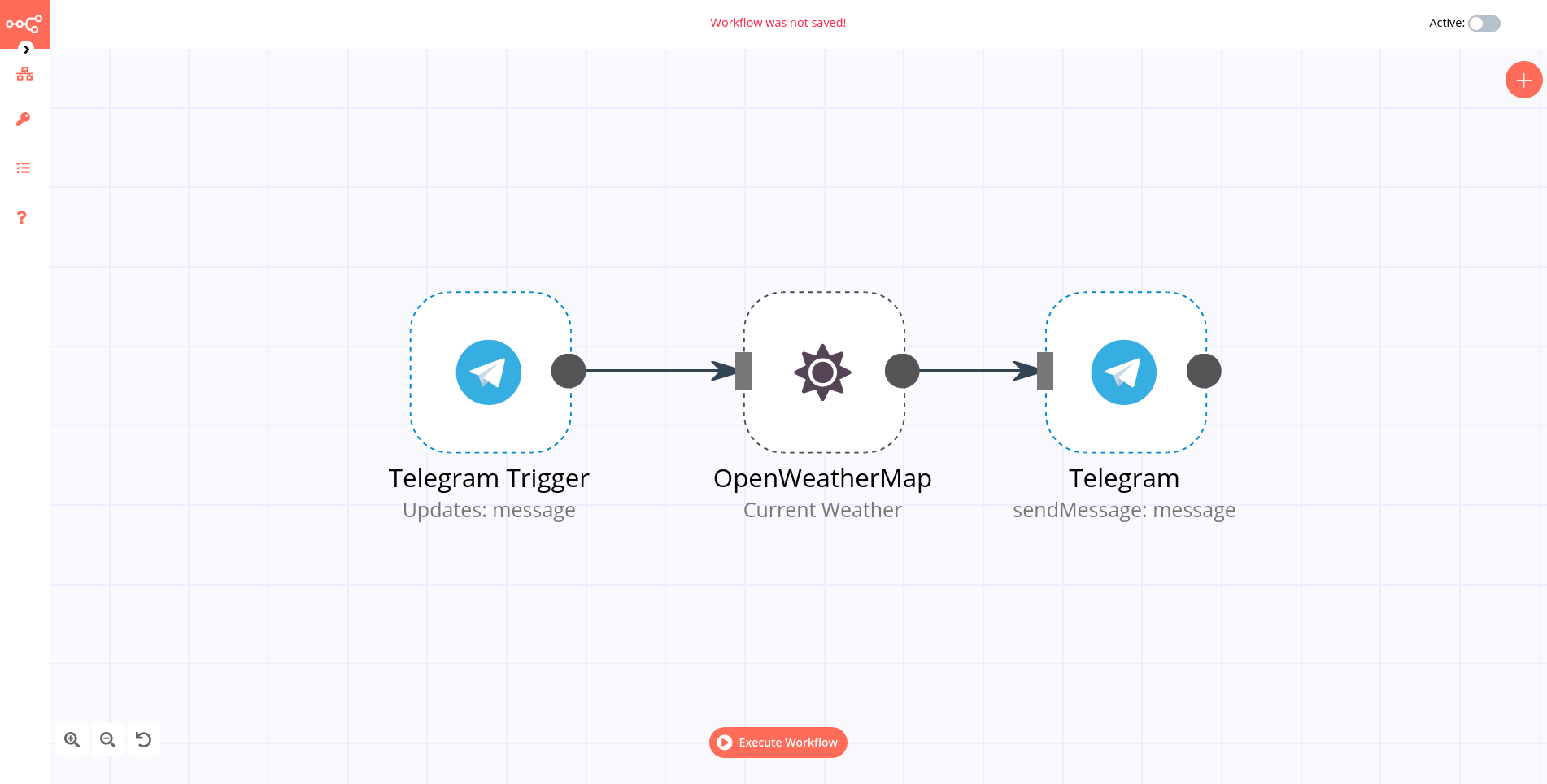
App Trigger nodes start the workflow when an event happens in an app. App Trigger nodes are named like the application they represent followed by “Trigger” and are listed under Trigger Nodes in the Editor. For example, a Telegram trigger node can be used to trigger a workflow when a message is sent in a Telegram chat.
Node settings
Nodes come with global operations and settings, as well as app-specific parameters that can be configured.
Operations
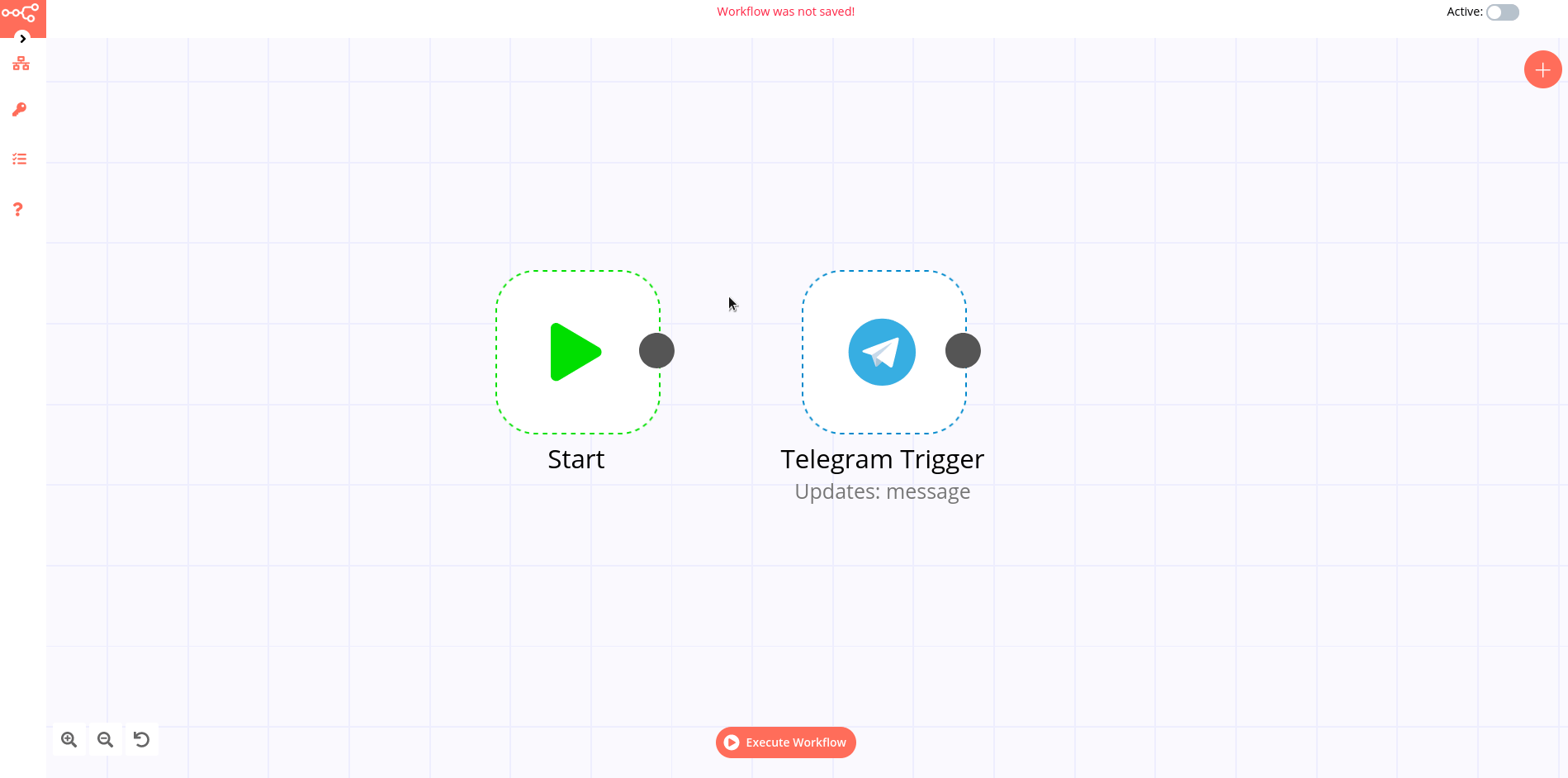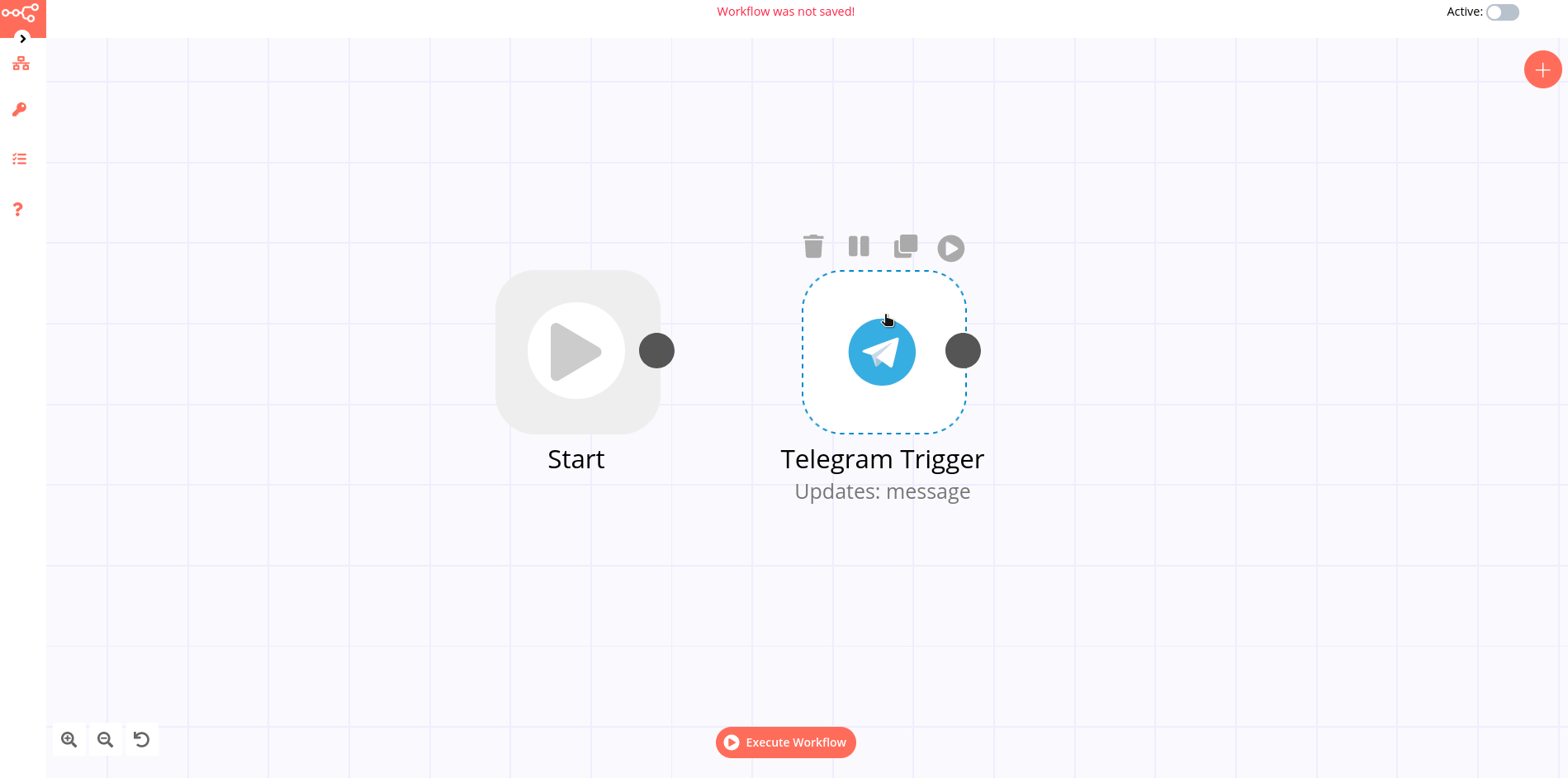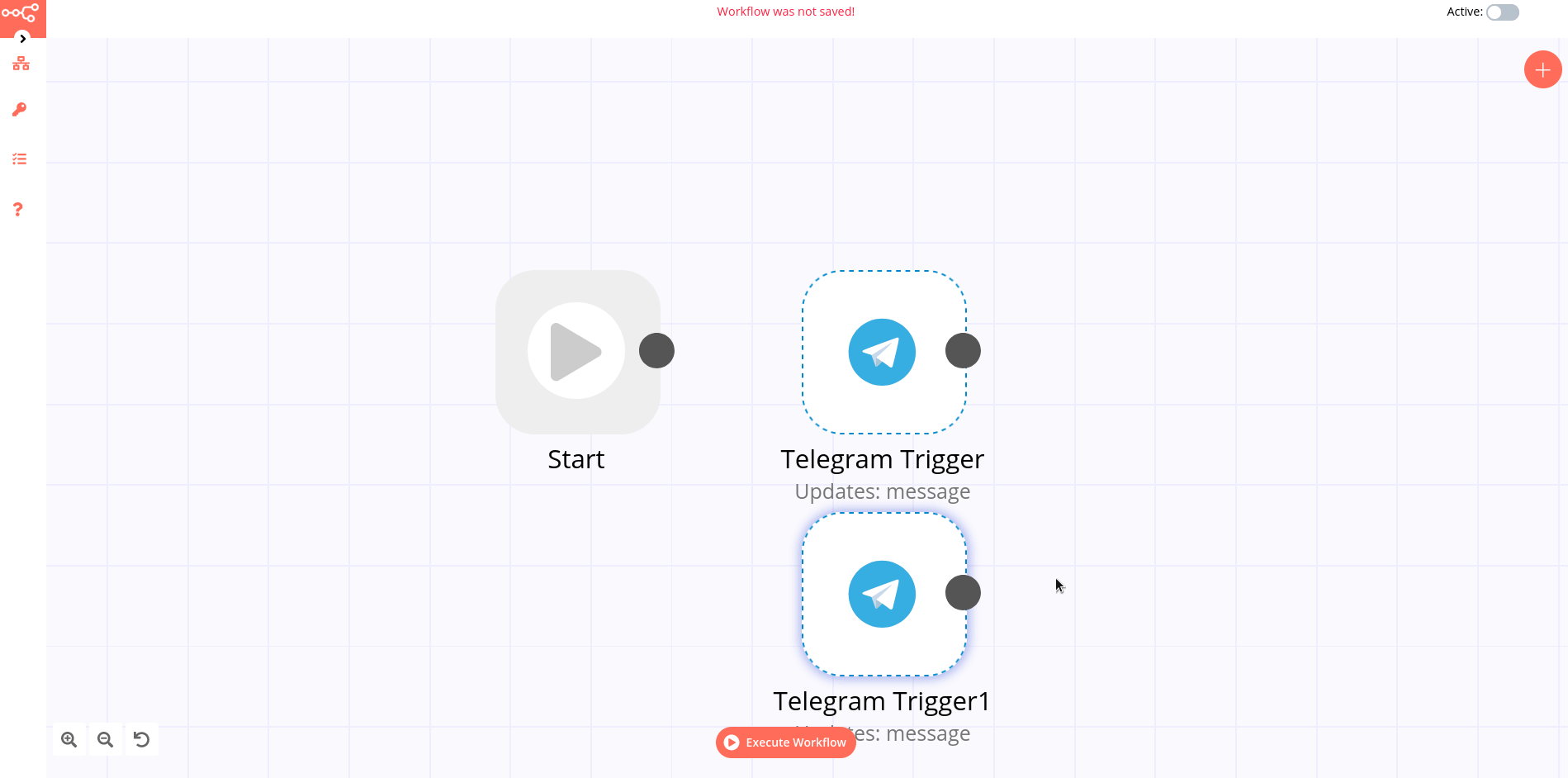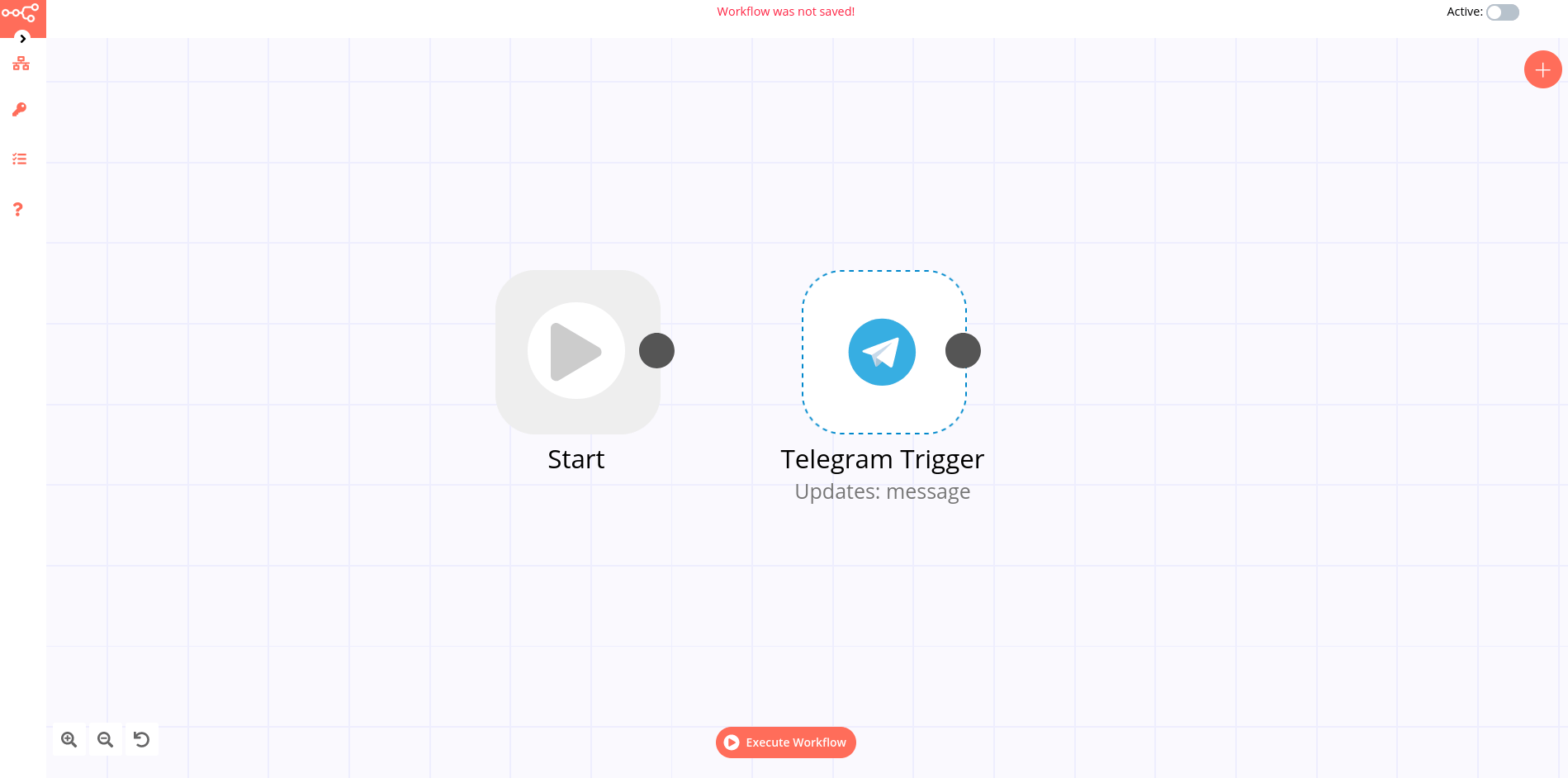
The node operations are illustrated with icons that appear on top of the node when you hover on it:
Delete: Remove the selected node from the workflow
Pause: Deactivate the selected node
Copy: Duplicate the selected node
Play: Run the selected node
To access the node parameters and settings, double-click on the node.
Parameters
The node parameters allow you to define the operations the node should perform. Find the available parameters of each node in the node reference.
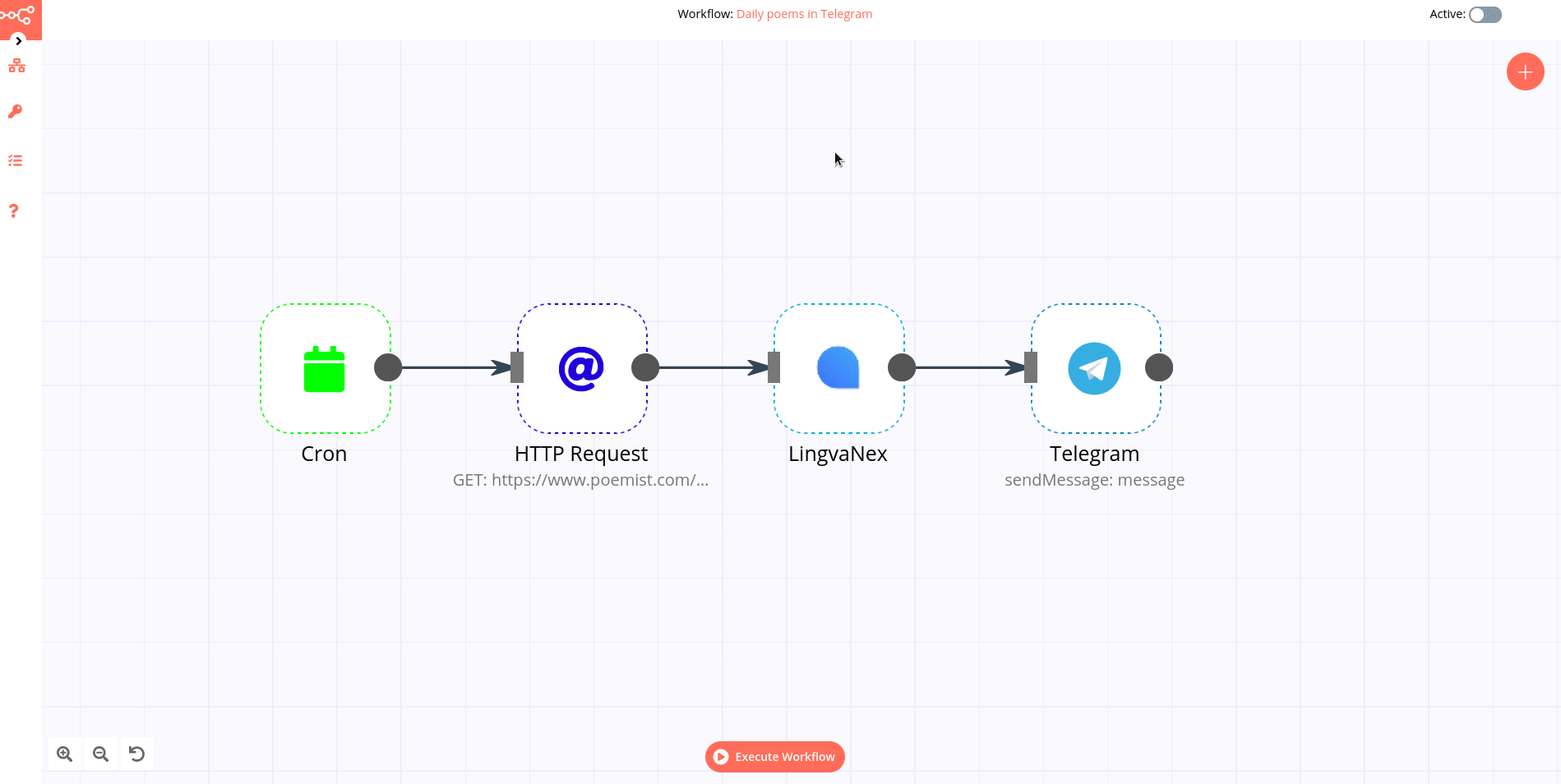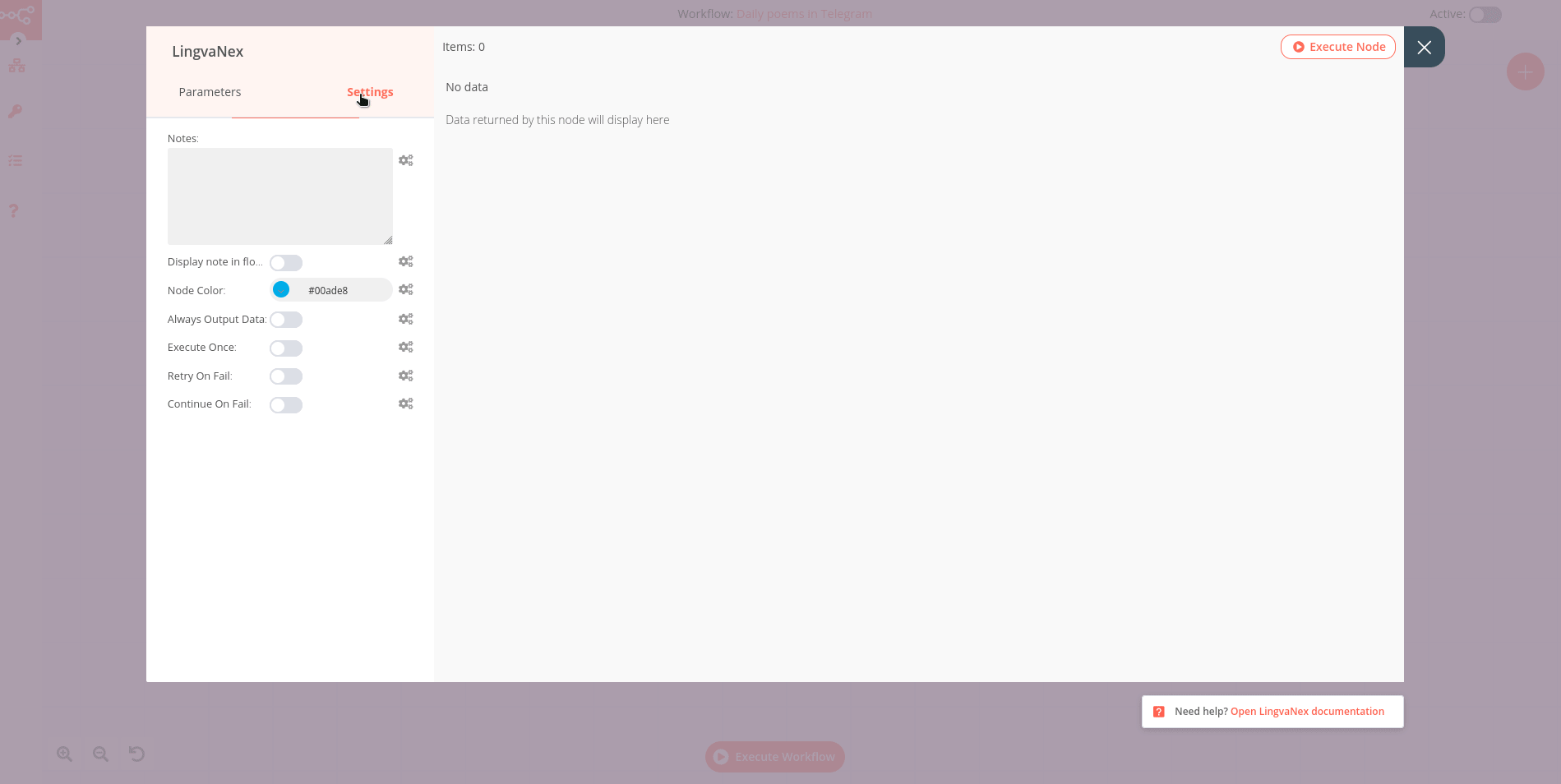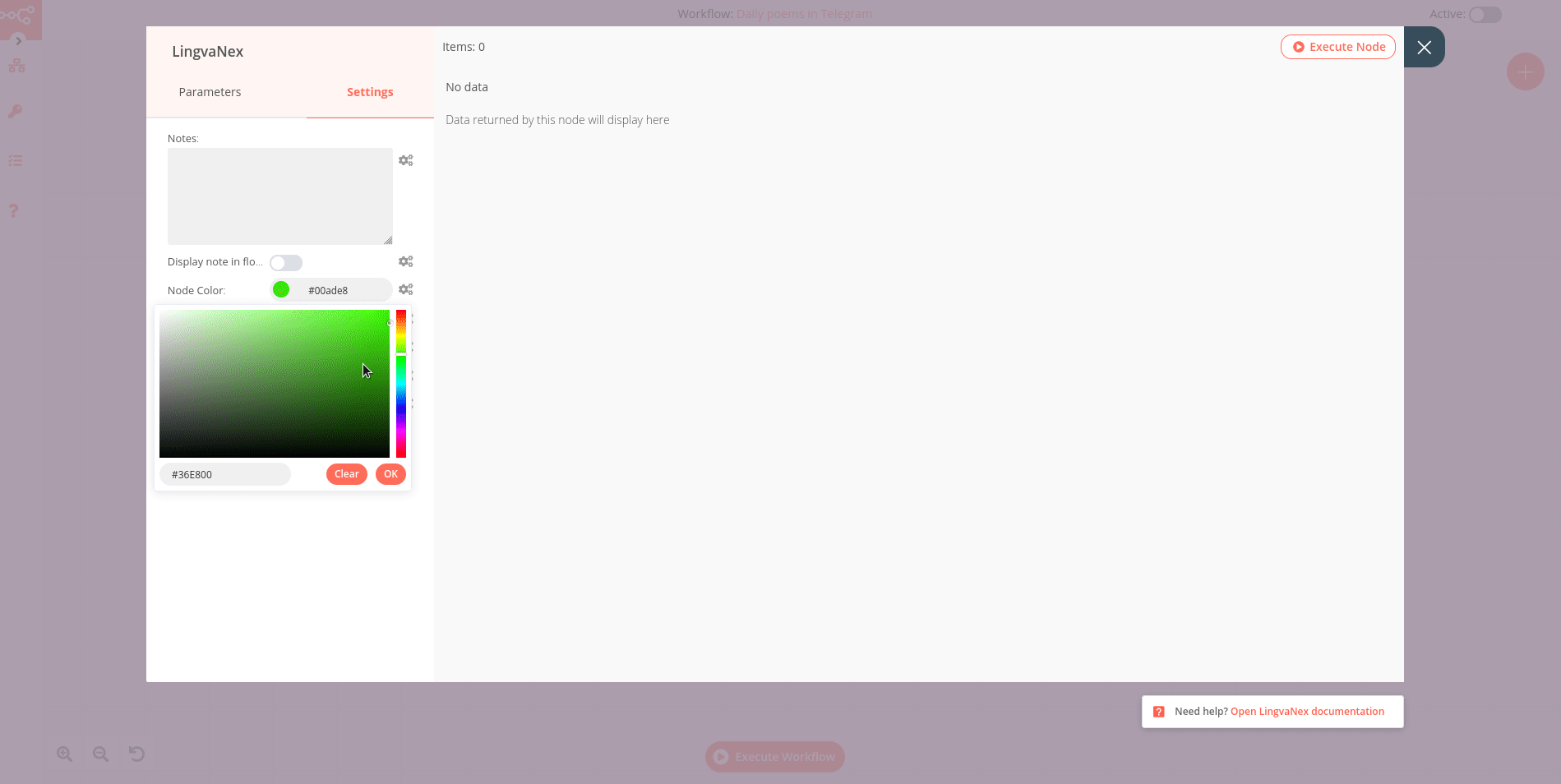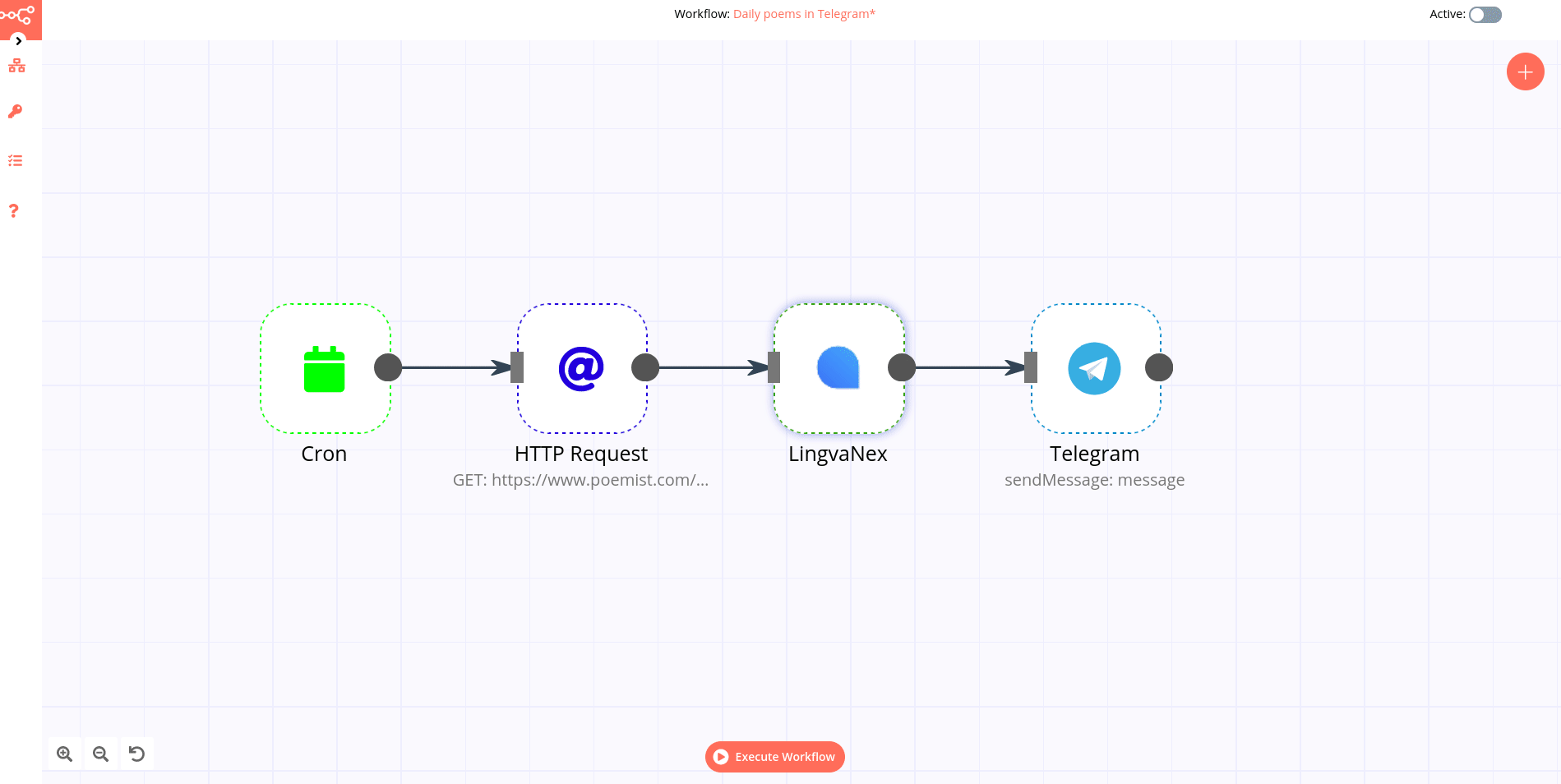
Settings
The node settings allow you to configure the look and execution of the node. The following options are available:
Notes: Optional note to save with the node
Display note in flow: If active, the note above will be displayed in the workflow as a subtitle
Node Color: The color of the node in the workflow
Always Output Data: If active, the node will return an empty item even if the node returns no data during an initial execution. Be careful setting this on IF nodes, as it could cause an infinite loop.
Execute Once: If active, the node executes only once, with data from the first item it receives.
Retry On Fail: If active, the node tries to execute a failed attempt multiple times until it succeeds
Continue On Fail: If active, the workflow continues even if the execution of the node fails. When this happens, the node passes along input data from previous nodes, so the workflow should account for unexpected output data.
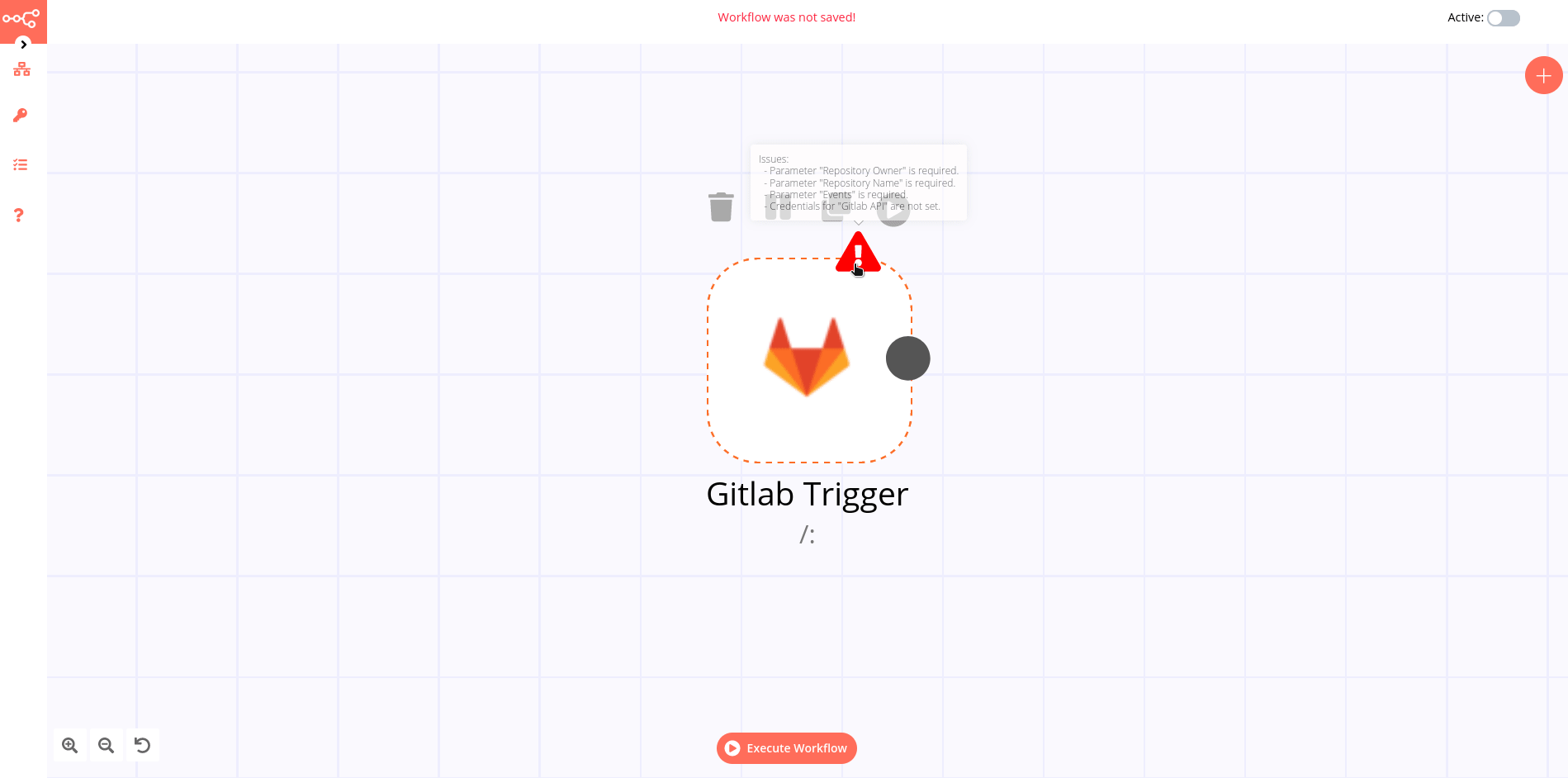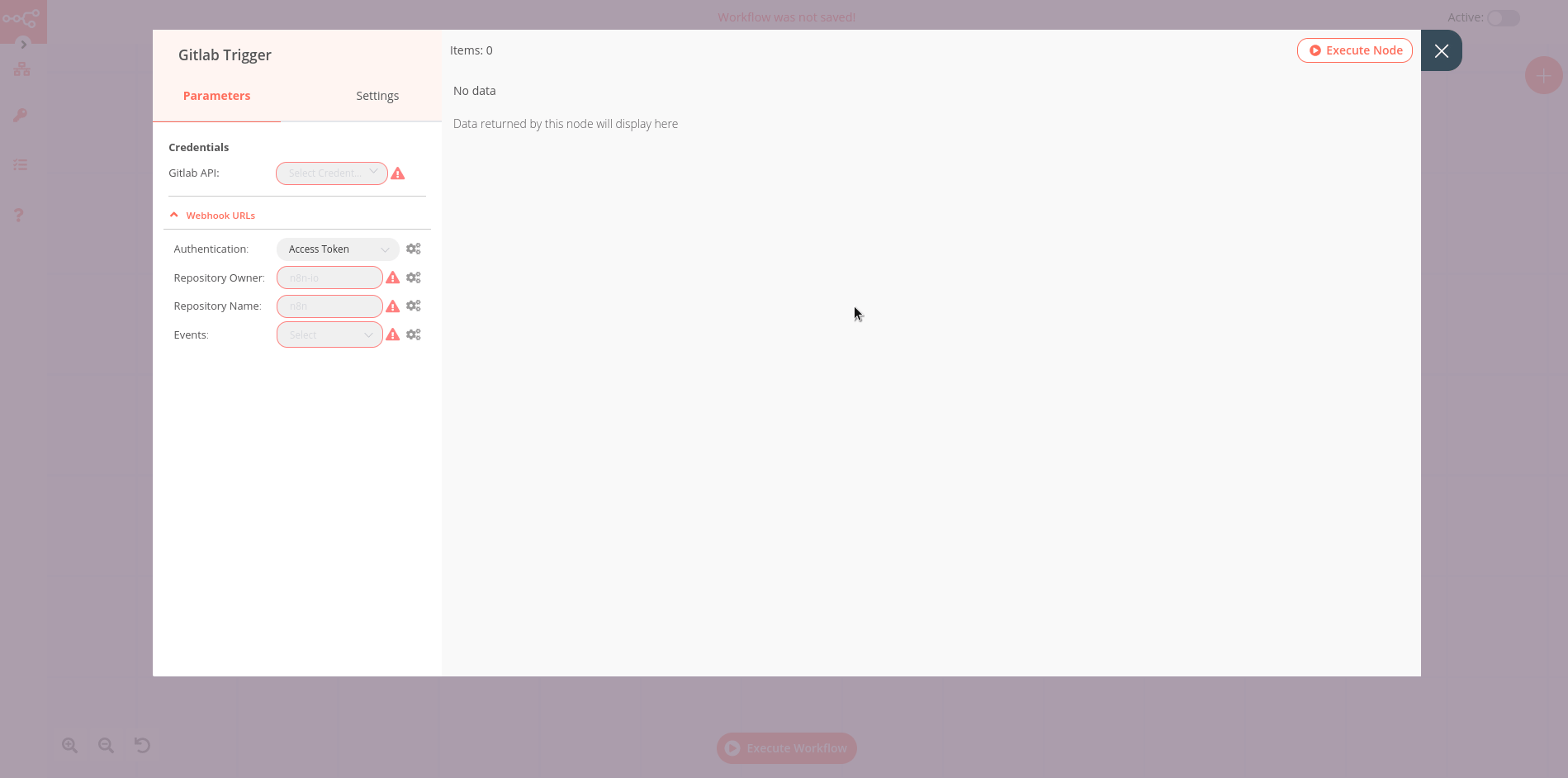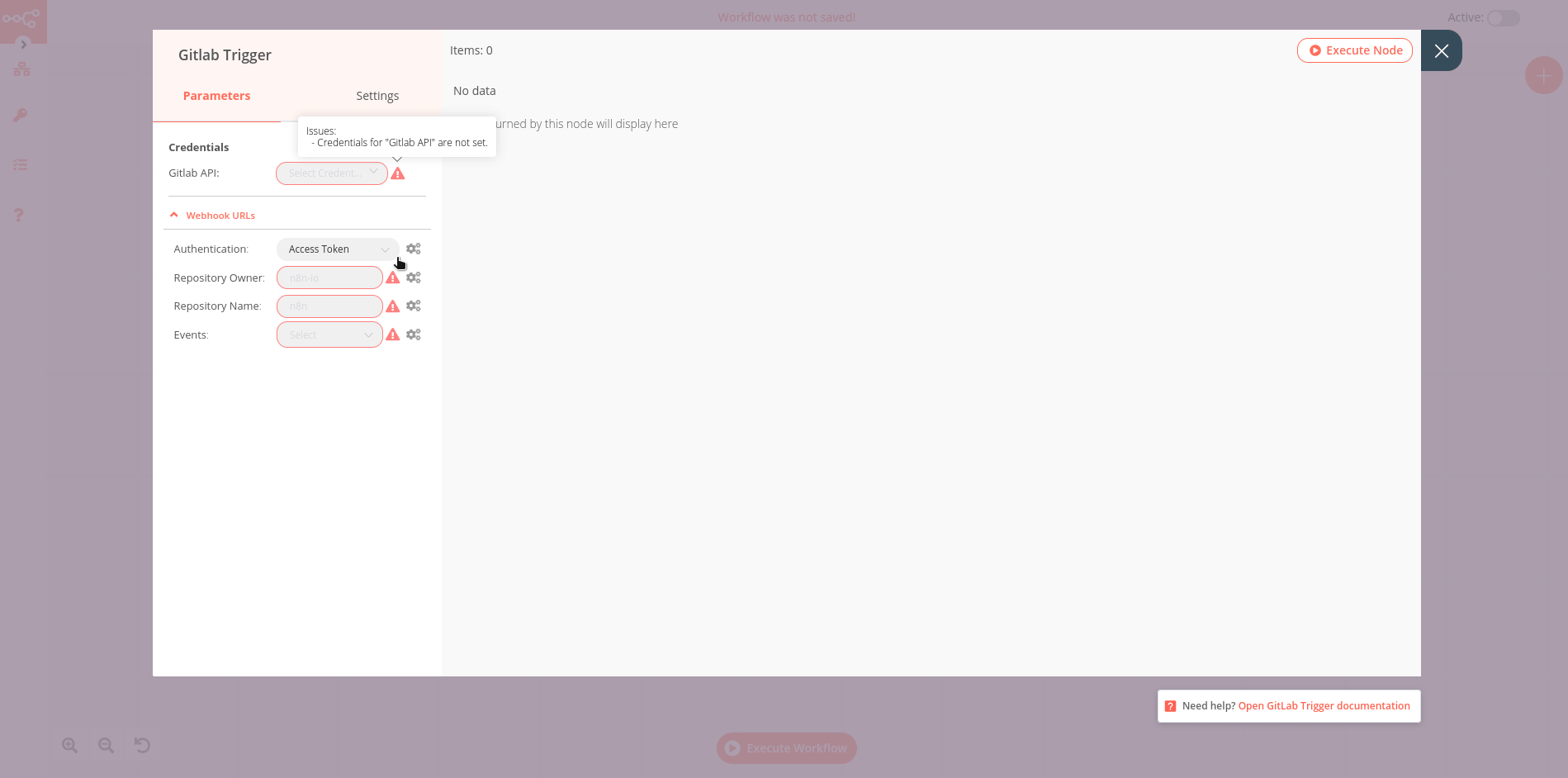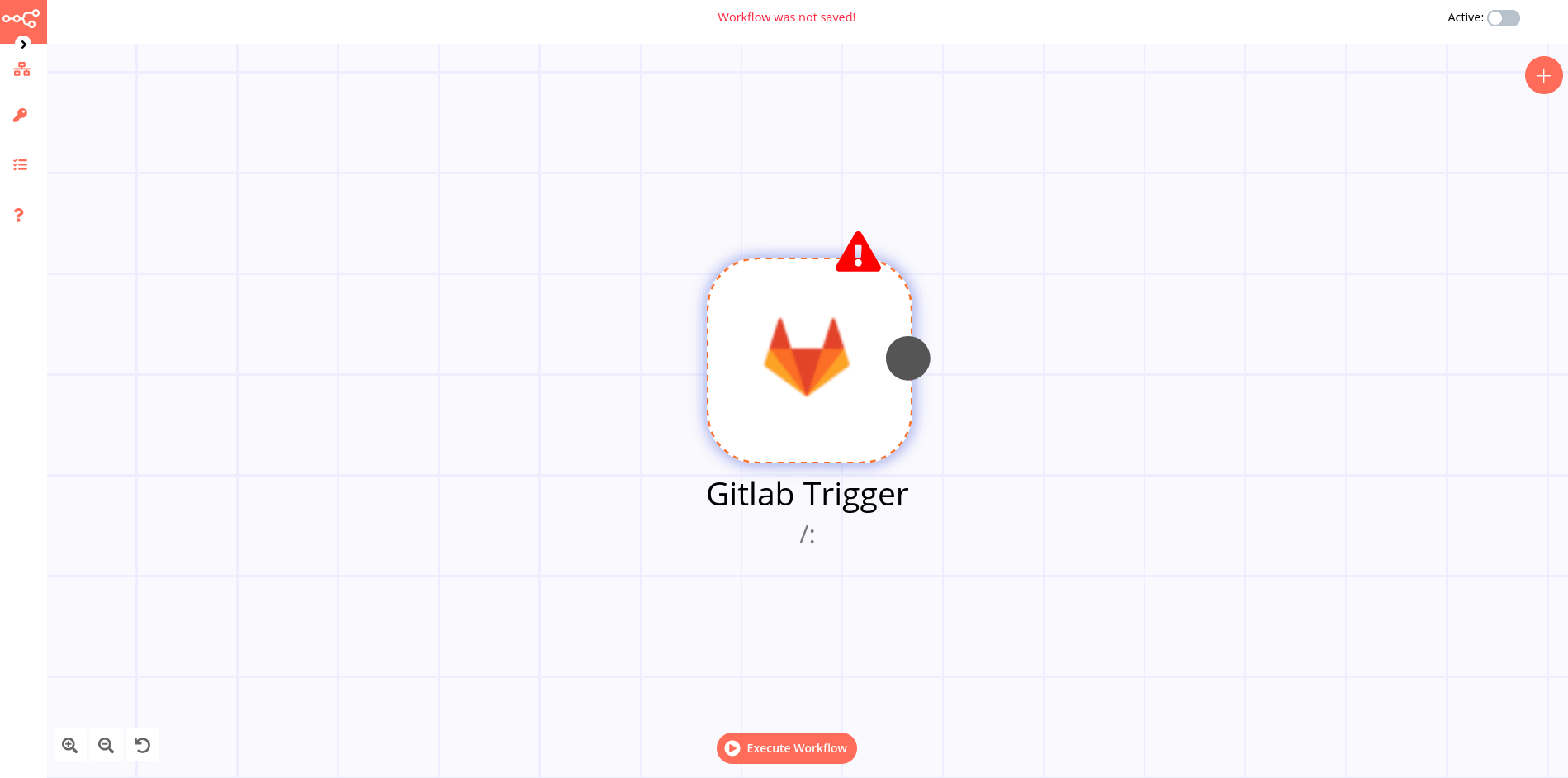
If a node is not correctly configured or is missing some required information, a warning sign is displayed on the top right corner of the node. To see what parameters are incorrect, double-click on the node and have a look at fields marked with red and the error message displayed in the respective warning symbol.
Workflow integration nodes
To boost your workflow automation you can connect with widely external nodes.
List of automation nodes:
Action Network
Activation Trigger
ActiveCampaign
ActiveCampaign Trigger
Acuity Scheduling Trigger
Affinity
Affinity Trigger
Agile CRM
Airtable
Airtable Trigger
AMQP Sender
AMQP Trigger
APITemplate.io
Asana
Asana Trigger
Automizy
Autopilot
Autopilot Trigger
AWS Comprehend
AWS DynamoDB
AWS Lambda
AWS Rekognition
AWS S3
AWS SES
AWS SNS
AWS SNS Trigger
AWS SQS
AWS Textract
AWS Transcribe
Bannerbear
Baserow
Beeminder
Bitbucket Trigger
Bitly
Bitwarden
Box
Box Trigger
Brandfetch
Bubble
Calendly Trigger
Chargebee
Chargebee Trigger
CircleCI
Clearbit
ClickUp
ClickUp Trigger
Clockify
Clockify Trigger
Cockpit
Coda
CoinGecko
Compression
Contentful
ConvertKit
ConvertKit Trigger
Copper
Copper Trigger
Cortex
CrateDB
Cron
Crypto
Customer Datastore (n8n training)
Customer Messenger (n8n training)
Customer Messenger (n8n training)
Customer.io
Customer.io Trigger
Date & Time
DeepL
Demio
DHL
Discord
Discourse
Disqus
Drift
Dropbox
Dropcontact
E-goi
Edit Image
Elastic Security
Elasticsearch
EmailReadImap
Emelia
Emelia Trigger
ERPNext
Error Trigger
Eventbrite Trigger
Execute Command
Execute Workflow
Facebook Graph API
Facebook Trigger
Figma Trigger (Beta)
FileMaker
Flow
Flow Trigger
Form.io Trigger
Formstack Trigger
Freshdesk
Freshservice
Freshworks CRM
FTP
Function
Function Item
G Suite Admin
GetResponse
GetResponse Trigger
Ghost
Git
GitHub
Github Trigger
GitLab
GitLab Trigger
Gmail
Google Analytics
Google BigQuery
Google Books
Google Calendar
Google Calendar Trigger
Google Cloud Firestore
Google Cloud Natural Language
Google Cloud Realtime Database
Google Contacts
Google Docs
Google Drive
Google Drive Trigger
Google Perspective
Google Sheets
Google Slides
Google Tasks
Google Translate
Gotify
GoToWebinar
Grafana
GraphQL
Grist
Gumroad Trigger
Hacker News
Harvest
HelpScout
HelpScout Trigger
Home Assistant
HTML Extract
HTTP Request
HubSpot
HubSpot Trigger
Humantic AI
Hunter
iCalendar
IF
Intercom
Interval
Invoice Ninja
Invoice Ninja Trigger
Item Lists
Iterable
Jira Software
Jira Trigger
JotForm Trigger
Kafka
Kafka Trigger
Keap
Keap Trigger
Kitemaker
Lemlist
Lemlist Trigger
Line
LingvaNex
LinkedIn
Local File Trigger
Magento 2
Mailcheck
Mailchimp
Mailchimp Trigger
MailerLite
MailerLite Trigger
Mailgun
Mailjet
Mailjet Trigger
Mandrill
Marketstack
Matrix
Mattermost
Mautic
Mautic Trigger
Medium
Merge
MessageBird
Microsoft Dynamics CRM
Microsoft Excel
Microsoft OneDrive
Microsoft Outlook
Microsoft SQL
Microsoft Teams
Microsoft To Do
Mindee
MISP
Mocean
Monday.com
MongoDB
Monica CRM
Move Binary Data
MQTT
MQTT Trigger
MSG91
MySQL
n8n Trigger
NASA
Netlify
Netlify Trigger
Nextcloud
No Operation, do nothing
NocoDB
Notion (Beta)
Notion Trigger (Beta)
One Simple API
OpenThesaurus
OpenWeatherMap
Orbit
Oura
Paddle
PagerDuty
PayPal
PayPal Trigger
Peekalink
Phantombuster
Philips Hue
Pipedrive
Pipedrive Trigger
Plivo
Postgres
PostHog
Postmark Trigger
ProfitWell
Pushbullet
Pushcut
Pushcut Trigger
Pushover
QuestDB
Quick Base
QuickBooks Online
RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ Trigger
Raindrop
Read Binary File
Read Binary Files
Read PDF
Reddit
Redis
Rename Keys
Respond to Webhook
RocketChat
RSS Read
Rundeck
S3
Salesforce
Salesmate
SeaTable
SeaTable Trigger
SecurityScorecard
Segment
Send Email
SendGrid
Sendy
Sentry.io
ServiceNow
Set
Shopify
Shopify Trigger
SIGNL4
Slack
sms77
Snowflake
Split In Batches
Splunk
Spontit
Spotify
Spreadsheet File
SSE Trigger
SSH
Stackby
Start
Stop and Error
Storyblok
Strapi
Strava
Strava Trigger
Stripe
Stripe Trigger
SurveyMonkey Trigger
Switch
Taiga
Taiga Trigger
Tapfiliate
Telegram
Telegram Trigger
TheHive
TheHive Trigger
TimescaleDB
Todoist
Toggl Trigger
TravisCI
Trello
Trello Trigger
Twake
Twilio
Twist
Twitter
Typeform Trigger
Unleashed Software
Uplead
uProc
UptimeRobot
urlscan.io
Vero
Vonage
Wait
Webex by Cisco
Webex by Cisco Trigger
Webflow
Webflow Trigger
Webhook
Wekan
Wise
Wise Trigger
WooCommerce
WooCommerce Trigger
Wordpress
Workable Trigger
Workflow Trigger
Write Binary File
Wufoo Trigger
Xero
XML
Yourls
YouTube
Zendesk
Zendesk Trigger
Zoho CRM
Zoom
Zulip